Figure 7.
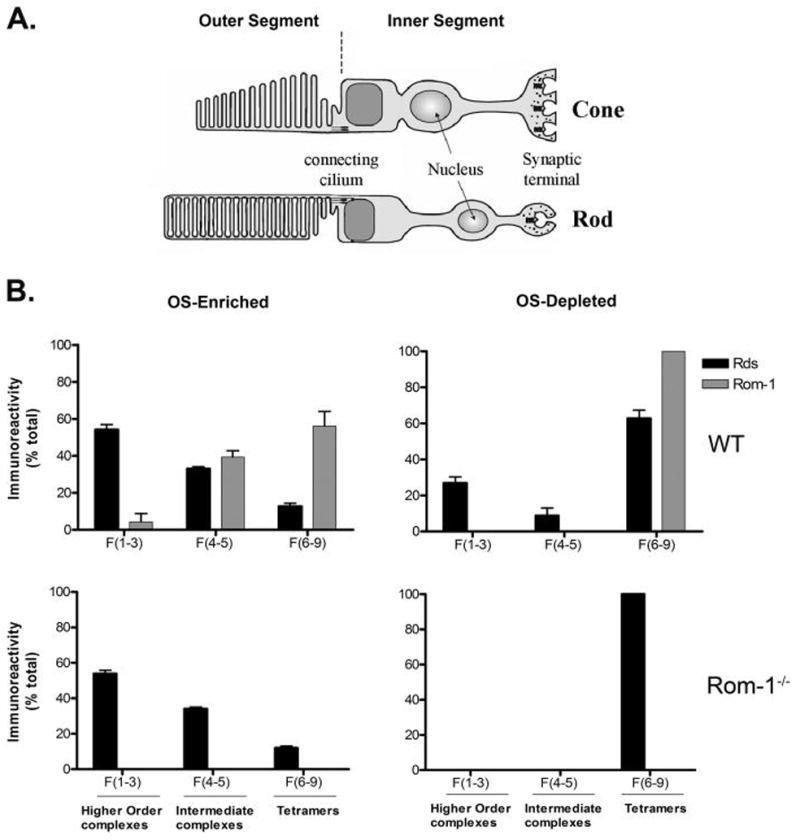
Summary illustration depicting the sites of Rds and Rom-1 complex formation in rod and cone photoreceptor cells. (A) Structural diagram of rod and cone photoreceptor cell. (B) Distribution of Rds complexes in OS-enriched and OS-depleted preparations from WT and Rom-1−/− retinas. The histograms summarize the results of the present study. Depending on the nature of the complex, Rds was recovered mostly as covalent disulfide-linked high order oligomers in the OS and noncovalent tetrameric complex in the IS from both models. Some of these complexes are homo complexes of Rds or hetero associations with Rom-1. The rearrangement from a noncovalent tetrameric complexes formed in the IS to a covalent octameric and oligomeric complexes formed in the OS would require the enzymatic action of an as yet unknown disulfide isomerase that should be located in the OS.
