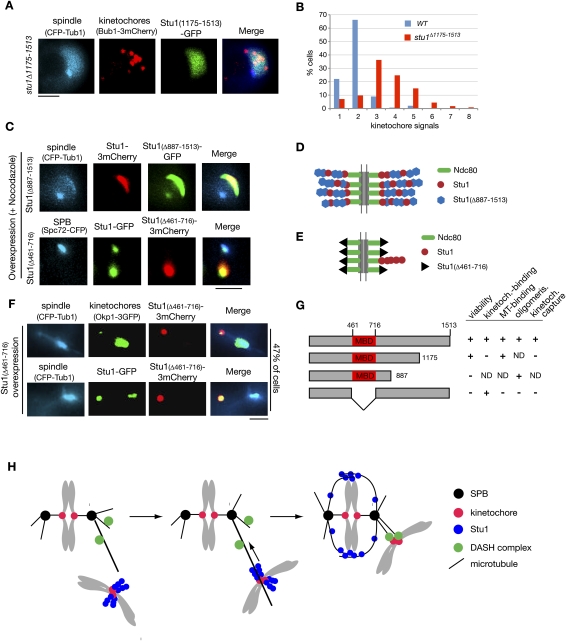
Figure 8.
Stu1 domain analysis. (A) C-terminal sequences are required for KT localization of Stu1. stu1Δ1175–1513 cells were analyzed 150 min after the release from G1 into nocodazole. Bar, 2 μm. (B) stu1Δ1175–1513 cells display an increased number of detached KTs per cell. Quantification of detached KTs or KT clusters in wild-type and stu1Δ1175–1513 cells processed as in A. n > 100. (C) Stu1 polymerization at detached KTs depends on Stu1's MBD (amino acids 461–716). Stu1Δ887–1513 and Stu1Δ461–716 were overexpressed from a GAL promoter in a wild-type STU1 background during a G1 arrest. Cells were analyzed 240 min after the release from G1 into nocodazole. Note that Stu1Δ887–1513 can still copolymerize with wild-type Stu1, whereas Stu1Δ461–716 cannot. Bar, 2 μm. (D,E) Putative models illustrating the phenotypes observed in C. (F) Overexpression of Stu1Δ461–716 results in detached KTs. Stu1Δ461–716 overexpression was as in C. Cells were analyzed 120 min after the release from G1. Bar, 2 μm. (G) Summary of Stu1 domain functions. (ND) Not done. (H) Model describing the role of Stu1 during KT capturing. For details, see the text.