Figure 5.
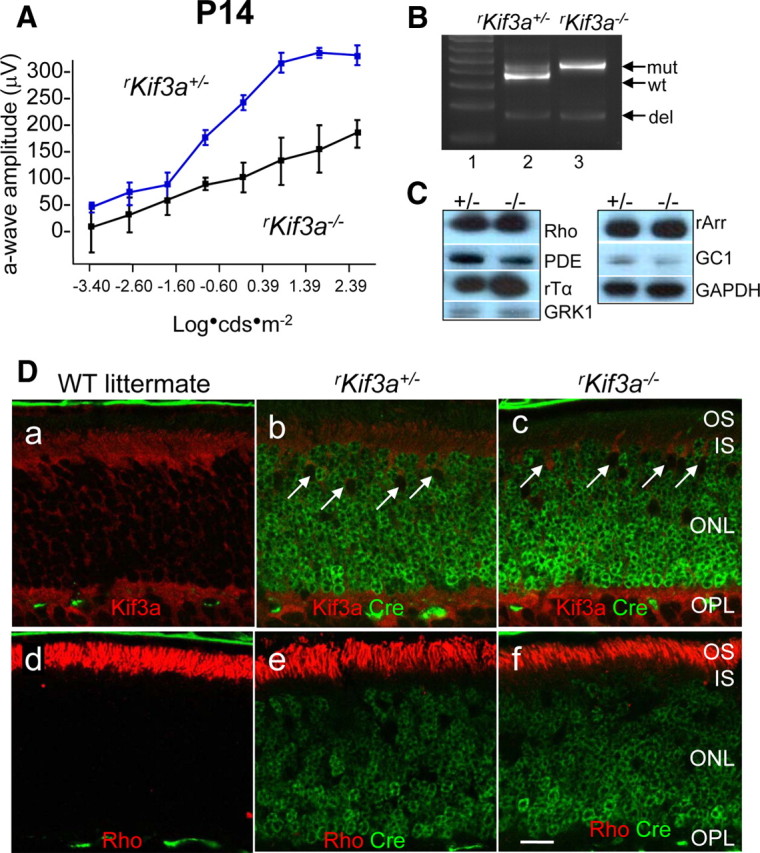
KIF3A deletion in P14 rod photoreceptors. A, Scotopic (dark-adapted) electroretinogram of P14 rKif3a+/− and rKif3a−/− mice. The rKif3a−/− a-wave amplitude, indicative of rod function, is attenuated relative to the WT a-wave response at all intensities tested. Error bars indicate SEM. B, PCR-based genotyping of rKif3a+/− (lane 2) and rKif3a−/− mice (lane 3) with primers P1, P2, and P3 and retina DNA as a template (see Materials and Methods) (Fig. 1A). P1 and P2 amplify the WT fragment (wt) and the mutant (insertion of loxP) fragment (mut) from rKif3a+/− DNA, but only the mutant fragment from rKif3a−/− DNA. P1 and P3 amplify the deletion fragment (del) appearing after excision of exon 2. Both the heterozygous and homozygous floxed mice show the deletion fragment at P14. Lane 1, MW standards. C, Immunoblots. Polypeptides of rKif3a+/− and rKif3a−/− retina lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE, blotted, and probed with anti-rhodopsin, anti-rod Tα, anti-rod PDE6, anti-GRK1, anti-rod arrestin, and anti-GC1. Anti-GAPDH served as a loading control. Note that the proteins levels are very similar in both from rKif3a+/− (+/−) and rKif3a−/− (−/−) lanes. D, Confocal immunolocalization of KIF3A and rhodopsin in P14 littermate WT (a, d), rKif3a+/− (b, e), and rKif3a−/− (c, f) cryosections imaged in the midperiphery. Retina sections were probed simultaneously with anti-Cre recombinase monoclonal antibody (green; b, c, e, f) and either anti-KIF3A (red; a–c) or anti-rhodopsin (red; d–f) polyclonal antibody. The white arrows (b, c) indicate examples of cone nuclei that do not express Cre recombinase. KIF3A is essentially undetectable in rKif3a−/− rod inner segments but present in cone inner segments, which are unaffected by the rod-specific deletion. Note prominent immunolabel for rhodopsin over rKif3a−/− rod outer segments that are reduced in length relative to WT. Several pyknotic nuclei were observed in the proximal rKif3a−/− ONL. Scale bar: a–f, 10 μm.
