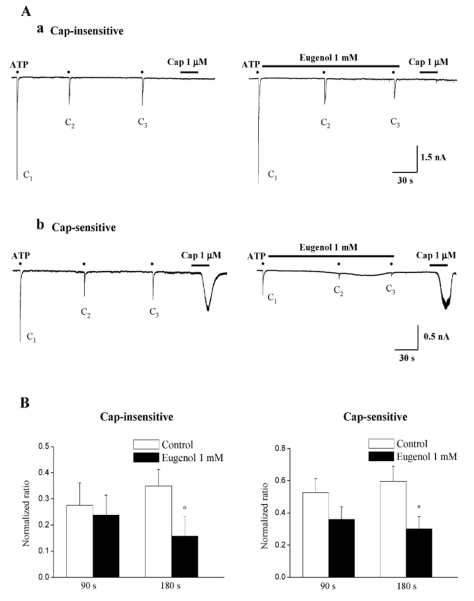
Fig. 2.
Eugenol inhibited ATP-induced P2X currents in both capsaicin-insensitive and capsaicin-sensitive rat TG neurons. (A) Representative current traces of 10 µM ATP-induced P2X currents under control (Aa and Ab, left), and eugenol (1 mM) (Aa and Ab, right) in both capsaicin-insensitive (Aa) and capsaicin-sensitive (Ab) rat TG neurons. (B) The summary of the inhibition of ATP-induced P2X currents in both capsaicin-insensitive (Ba) and capsaicin-sensitive (Bb) rat TG neurons. The amplitude of second (C2) and third currents (C3) was normalized compared to the first one (C1). Eugenol-induced inhibition in capsaicin-insensitive neurons (n=15) was similar to that obtained in capsaicin-sensitive neurons (n=10) (mean±SEM, p>0.05). Black points indicate the time point of ATP application.