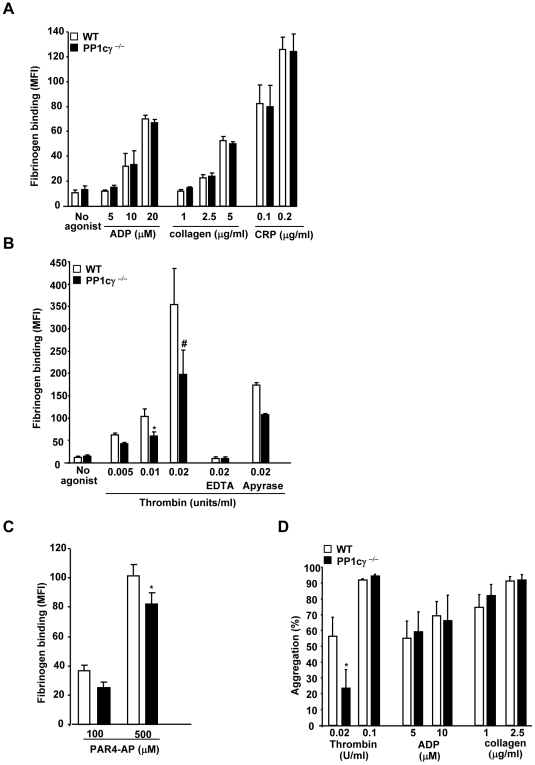
Figure 2. Thrombin specific impairment in soluble fibrinogen binding and aggregation in PP1cγ−/− platelets.
Washed platelets from WT or PP1cγ−/− mice were stimulated with ADP, collagen or CRP (A), thrombin (B) or PAR4-AP (C) in the presence of Alexa 488 fibrinogen and bound fibrinogen analyzed by flow cytometry as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). Data are ±SEM of 9–11 experiments for ADP, thrombin and collagen and 13–14 experiments for PAR4-AP. As compared to the WT platelets, the decreased fibrinogen binding in PP1cγ−/− platelets were significant at *p = 0.02 (for 0.01 U/ml thrombin); #p = 0.01 (for 0.02 U/ml thrombin); *p = 0.05 (for 200 µM PAR4-AP). In other experiments (n = 3), platelets were pretreated with 0.5 mM EDTA or 2 mM apyrase (ADP scavenger) prior to stimulation with 0.02 U/ml thrombin. (D) Percentage aggregation for WT and PP1cγ−/− platelets in response to the indicated doses of thrombin, ADP and collagen. Studies are indicated as ±SEM of 5–6 experiments. The decreased aggregation in 0.02 U/ml thrombin stimulated PP1cγ−/− platelets compared to WT platelets was significant at *p = 0.04.