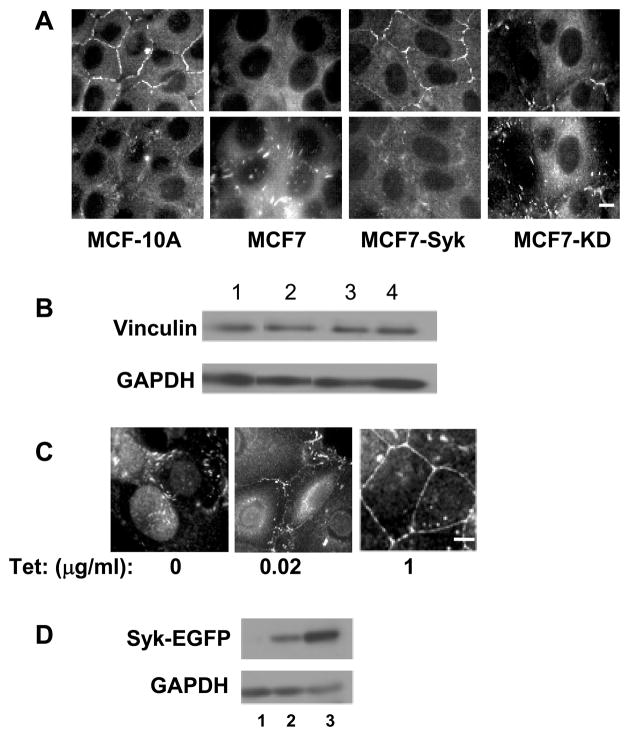
Figure 2.
The expression of Syk causes a redistribution of vinculin. A, MCF10A, MCF7, and MCF7 cells expressing Syk-EGFP (MCF7-Syk) or Syk-EGFP(K396R) (MCF7-KD) were grown on glass coverslips, fixed, stained for vinculin and examined by fluorescence microscopy. Two focal planes including cell-cell contacts (upper panels) or focal adhesions (lower panels) are shown. B, Western blotting analysis of vinculin and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) in lysates from MCF10A (lane 1), MCF7 (lane 2), MCF7-Syk (lane 3) and MCF7-KD (lane 4) cells. The images are derived from the same gel and blot, but, with the exception of lanes 3 and 4, are from nonadjacent lanes. C, Tet-response MCF7 cells were untreated (0) or treated with 20 ng/ml (0.02) or 1 μg/ml (1) tetracycline to induce expression of Syk-EGFP. Cells grown on untreated coverslips were fixed, stained for vinculin and examined by fluorescence microscopy. D, Western blotting analysis of Syk-EGFP and GAPDH in lysates of Tet-responsive MCF7 cells that were untreated (lane 1) or treated with 20 ng/ml (lane 2) or 1 μg/ml (land 3) tetracycline to induce expression of Syk-EGFP. Bars = 10μm.