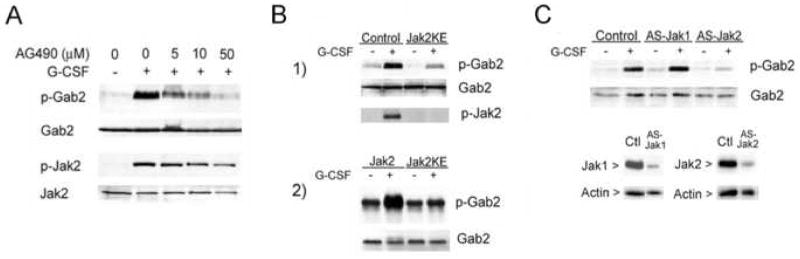
Figure 2. Effect of Jak2 inhibition on G-CSF-stimulated Gab2 tyrosine phosphorylation.
A. Treatment with the Jak inhibitor AG490 resulted in a concentration-dependent reduction in G-CSF-stimulated Gab2 phosphorylation. DT40GR cells were serum starved 15 hours, treated with indicated concentrations of AG490 and stimulated (+) or not (−) with G-CSF. Cell lysates were evaluated by sequential Western blotting with antibodies to phosphoGab2 (p-Gab2), total Gab2 protein, phosphoJak2 (p-Jak2), and total Jak2 protein.
B. G-CSF strongly stimulated Gab2 phosphorylation in cells transfected with wild-type Jak2, but not in cells transfected with the kinase-inactive, dominant negative Jak2KE mutant. Gab2 phosphorylation was evaluated in cells transfected with a kinase-inactive, dominant negative mutant of Jak2 (Jak2KE). (1) DT40GR cells transfected with vector alone (control) or the dominant negative Jak2 mutant (Jak2KE) were stimulated (+) or not (−) with G-CSF. Following SDS-PAGE, cell lysates were evaluated by sequential Western blotting using antibodies to detect phosphorylated Gab2 (p-Gab2, upper panel), total Gab2 protein (middle panel), and phosphorylated Jak2 (p-Jak2, bottom panel). Cells transfected with Jak2KE showed inhibition of both Jak2 and Gab2 phosphorylation in response to G-CSF. (2) Human 293 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding Flag-tagged Gab2, HA-tagged G-CSF receptor, and either wild-type Jak2 or the Jak2KE mutant. Approximately 48 hours after transfection, cells were serum-starved for four hours, stimulated (+) or not (−) with G-CSF for 5 minutes, and lysed. An aliquot of each lysate was analyzed by blotting for the HA epitope tag; this confirmed equivalent G-CSF receptor expression (not shown). Transfected Gab2 was precipitated from the lysates using antibody to the Flag epitope tag. The anti-Flag immunoprecipitates were evaluated by blotting, using antibodies to phosphotyrosine to detect phosphorylated Gab2 (p-Gab2) and anti-Gab2 to evaluate total Gab2 protein.
C. DT40GR cells stably transfected with vector alone (control), antisense Jak1 (ASJak1), or antisense Jak2 (ASJak2) were treated (+) or not (−) with G-CSF for 5 min. Following SDS-PAGE, cell lysates were evaluated by sequential Western blotting for detection of phosphorylated Gab2 (p-Gab2) and then total Gab2 protein (Gab2). G-CSF-stimulated Gab2 phosphorylation was selectively inhibited by inhibition of Jak2 expression. Below are shown results of Western blots for Jak1 (left) or Jak2 (right) in lysates from vector transfected control DT40GR cells (Ctl), Jak1 antisense-transfected DT40GR cells (AS-Jak1), and Jak2 antisense-transfected DT40GR cells (AS-Jak2). These demonstrate the decrease in Jak1 and Jak2 expression by cells transfected with their respective antisense constructs. The results for control and ASJak1 samples are from the same gel, but were separated by additional lanes; only the relevant lanes are shown in order to facilitate comparison. The membranes were stripped and reprobed with anti-Actin antibodies as indicated.