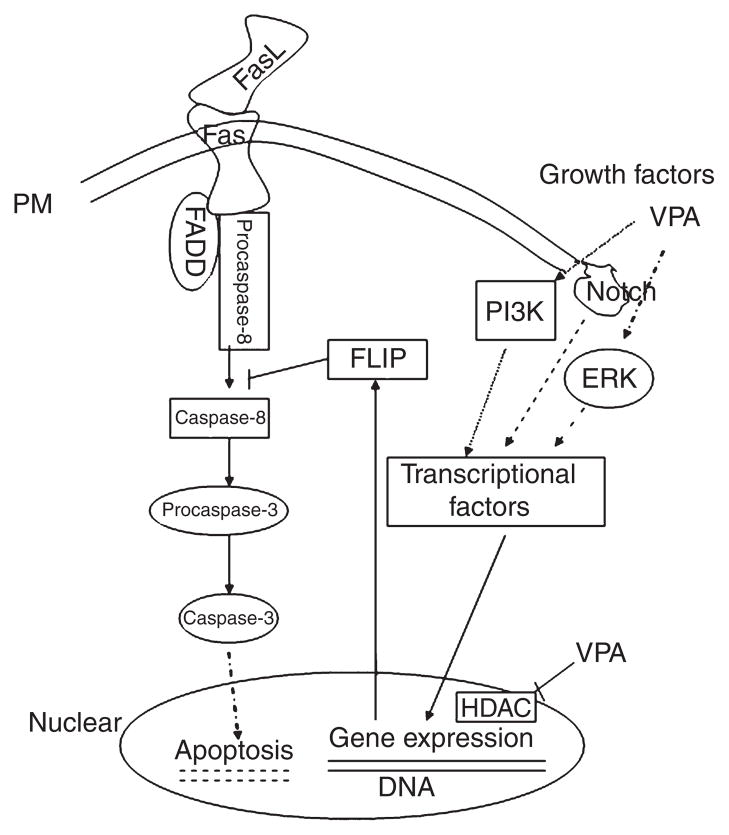
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of valproate’s intracellular cytoprotective mechanisms. Fas ligand (FasL)/Fas interactions cause effector caspase activation. FasL-mediated apoptosis can be blocked by the inhibition of caspase-8 protease through cellular Fas-associated death domain-like interleukin- 1-beta-converting enzyme-inhibitory protein (c-FLIP). Valproate (VPA) activates mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and PI- 3K pathways, which upregulate Notch3, c-FLIP, and other proteins (Bcl-2, BDNF, etc.) via transcriptional factors. VPA also regulates gene expression by inhibiting histone deacetylase (HDAC). Hatched lines represent membrane; dotted lines represent indirect effects. FADD = Fas-associated death domain- containing protein.