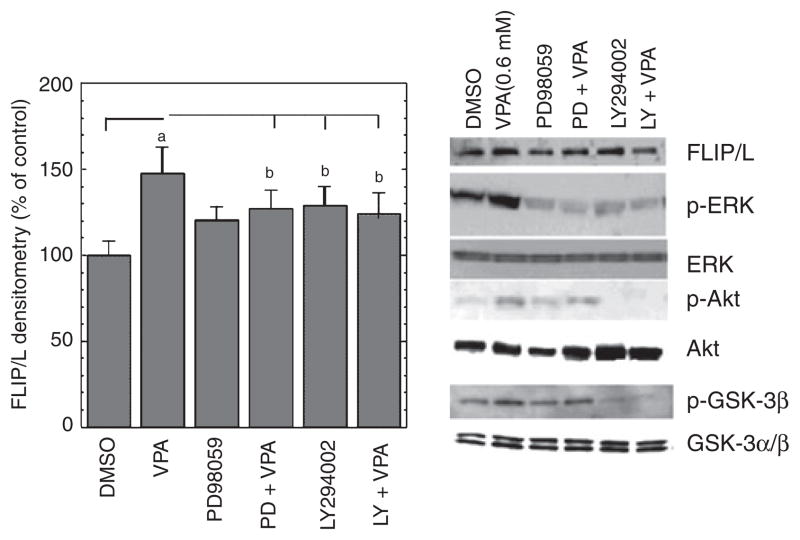
Fig. 7.
Valproate (VPA) activates extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI-3K) signal pathways in human vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC), and specific inhibitors of MEK and PI-3K abolish VPA’s upregulation of c-FLIP. Human VSMC were cultured in growth media close to confluence. The media were then replaced with serum-free media, and the cells were treated with VPA (0.8 mM) in the absence or presence of indicated inhibitors for two days. Immunoblotting was conducted as described in Materials and Methods. MEK inhibitor PD98059 (50 μM) and PI-3K inhibitor LY294002 (20 μM) attenuated VPA-induced increases in c-FLIP/L, phospho-ERK1/2 (P-p44/42), phospho-Akt, and phospho-GSK-3β, ap < 0.01, bp < 0.05, compared with cells treated with dimethy sulfoxide (DMSO, final concentration 0.1%) alone. Total ERK1/2 (p44/42), Akt, and GSK-3 α/β levels did not change significantly.