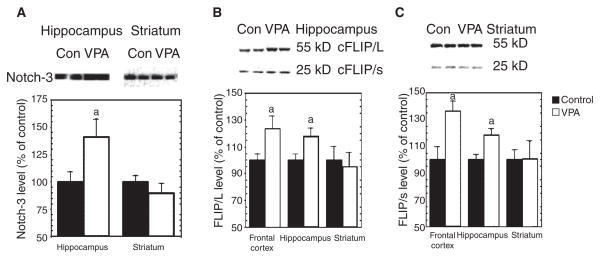
Fig. 8.
Valproate (VPA) activates Notch3 signaling in vivo. Adult male Wistar rats received VPA chow for four weeks. Protein extracts from frontal cortex, hippocampus, or striatum were separated on SDS-PAGE, and then immunoblotted with anti-Notch3 or anti-cellular Fas-associated death domain-like interleukin-1-beta-converting enzyme-inhibitory protein (c-FLIP) antibody. The resultant bands were quantified and standardized by bands of β-actin. (A) VPA significantly increased cleaved Notch3 protein levels in hippocampus [t(22) = 2.51, p = 0.02], but not striatum. (B) VPA significantly increased c-FLIP/L and c-FLIP/s levels in rat frontal cortex and hippocampus (ap < 0.05 versus control), but not in striatum. (C) Representative blot with frontal cortex samples was similar to that of hippocampal samples.