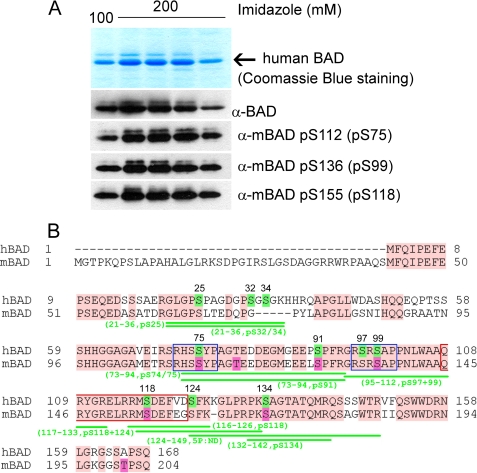
FIGURE 1.
Analysis of in vivo phosphorylation of purified human BAD protein. A, purification of human BAD from Sf9 insect cells. The top panel shows Coomassie Blue staining after SDS-PAGE of human BAD obtained by elution from nickel-agarose beads by 100 and 200 mm imidazole, respectively. The phosphorylation of serines 75, 99, and 118 was verified by use of phosphospecific antibodies. B, sequence alignment of human and murine BAD protein and mass spectrometry analysis of phosphopeptides obtained by tryptic and GluC digestion of hBAD. For a detailed list of identified phosphopeptides, see also Table 1. The putative phosphorylation sites of human BAD are highlighted in green, and their positions within the sequence are indicated by numbers. The published phosphorylation sites of murine BAD are highlighted in magenta. The conserved regions between human and murine BAD are shown in pink. The putative 14-3-3 binding sites are indicated by blue rectangles, and the conserved BH3 domains are shown by red rectangles.