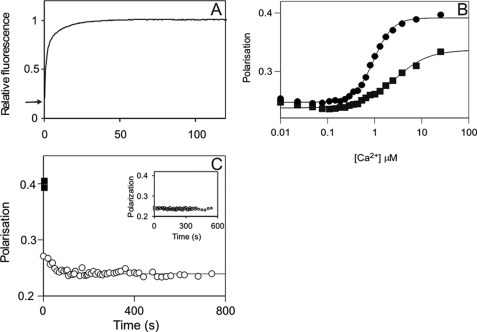
FIGURE 4.
Mechanism of CaM dissociation from its complex with phospho-Thr286-αCaMKII upon Ca2+ sequestration. A, calmodulin stretching shown by DA-CaM unquenching. The mixture of 1 μm αCaMKII, 1 μm DA-CaM, and 0.5 mm ATP in 50 mm K-PIPES, pH 7.0, 100 mm KCl, 2 mm MgCl2, 1 mm 1,4-dithiothreitol, and 0.1 mm CaCl2 was rapidly mixed with 50 mm EGTA adjusted to pH 7.0 with KOH at 21 °C. DA-CaM fluorescence (donor AEDANS was excited at 365 nm, and emission was detected using a 455 nm cut-off filter) was quenched in complex with phospho-Thr286-αCaMKII. The arrow indicates relative fluorescence 0.2. Upon EGTA addition, DA-CaM fluorescence was unquenched in a biphasic process. B, polarization of FL-CaM upon Ca2+-dependent binding to αCaMKII (squares) and CaMKIV (diamonds). The mixture of 120 nm FL-CaM and 1.4 μm CaMKIV or 2.0 μm αCaMKII in the same conditions as above except for the presence of 2 mm EGTA was titrated with CaCl2. [Ca2+] was determined as described under “Materials and Methods” (19). C, FL-CaM dissociation from phospho-Thr286-αCaMKII was monitored by polarization. ■, the starting values of polarization of the Ca2+/FL-CaM·phospho-Thr286-αCaMKII; the time course of polarization decay (○) upon the addition of 4.2 mm EGTA is shown. Inset, controls that contained no ATP but in which 2 mm EGTA was present from the start (n = 4); these show no time-dependent change. In the main panel, a mean rate constant of 0.0200 ± 0.0075 s−1 (±S.D.) was obtained for the polarization data on CaM dissociation (n = 5).