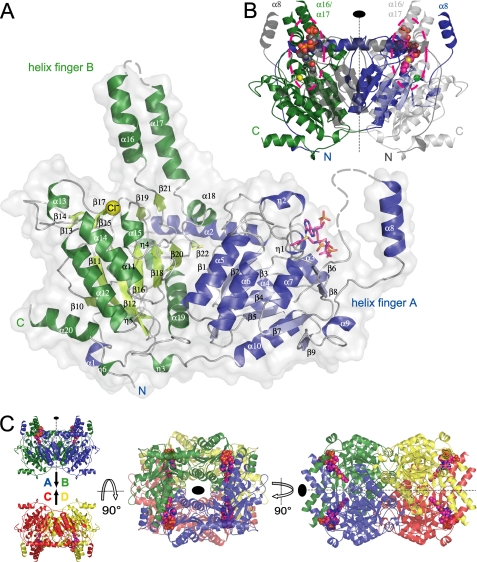
FIGURE 4.
A, overall structure of the C. symbiosum GcdA monomer. α- and 310-helices of the N-terminal domain are colored blue, the respective β-strands are shown in lighter blue. The secondary structure motifs of the C-terminal domain are represented in dark green (helices) and light green (β-strands). The bound crotonyl-CoA is displayed as a magenta stick model and the chloride ion bound to OAH2 is shown as a yellow sphere. Residues missing in the electron density are indicated by broken lines. B, GcdA dimer. N and C terminus of the symmetry-equivalent chain B are colored dark and light gray, respectively. The crotonyl-CoA molecules at the dimer interfaces are represented as CPK models. The second chloride ion is displayed as a green sphere. The positions of the active sites are highlighted by dashed lines. C, two orthogonal orientations of the 222-symmetric GcdA tetramer deduced from the crystal packing. Chains A to D are colored blue, green, red, and yellow, respectively.