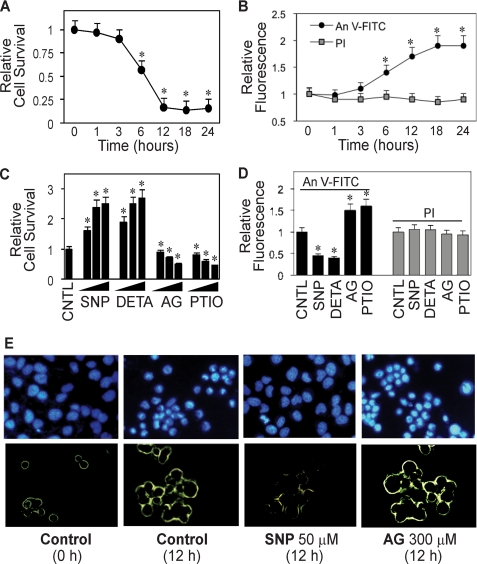
FIGURE 1.
Detachment-induced apoptosis and its inhibition by NO. A, effect of cell detachment on cell survival determined by XTT assay. Lung epithelial H460 cells were detached as described under “Materials and Methods” and suspended in HEMA-coated plates for various times (0–24 h). B, effect of cell detachment on apoptosis and necrosis determined by flow cytometry using annexin V-FITC (An V-FITC) and PI assays. C, effect of NO modulators on detachment-induced cell death. Detached cells were treated with various concentrations of NO donor, SNP (10, 50, 100 μm), or DETA NONOate (10, 50, 100 μm) or with NO inhibitor, AG (100, 200, 300 μm), or PTIO (10, 50, 100 μm) for 12 h. Cell survival was then determined by XTT assay. CNTL, control. D, effects of NO modulators on detachment-induced apoptosis and necrosis. Detached cells were treated with SNP (50 μm), DETA NONOate (50 μm), AG (300 μm), or PTIO (50 μm) for 12 h, and cell apoptosis and necrosis were determined as described above. E, upper panel, effect of NO modulators on detachment-induced apoptosis determined by Hoechst 33342 nuclear fluorescence staining. Lower panel, effect of NO modulators on detachment-induced apoptosis determined by annexin V-FITC fluorescence microscopy. Data are the mean ± S.D. (n = 3). *, p < 0.05 versus non-treated control.