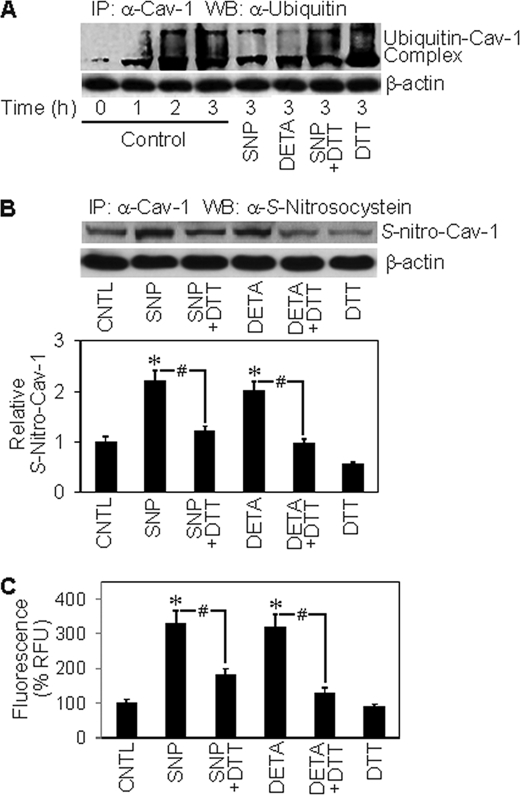
FIGURE 5.
Effects of NO modulators on Cav-1 ubiquitination and S-nitrosylation. A, H460 cells were detached and either left untreated or treated with SNP (50 μm) or DETA NONOate (50 μm) in the presence or absence of DTT (1 mm) in HEMA-coated plates. Cells lysates were prepared and immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-Cav-1 antibody. The resulting immune complexes were then analyzed for ubiquitin by Western blotting (WB) at various times. Maximum ubiquitination of Cav-1 was observed at ∼3 h after cell detachment. Lysate input was determined by probing β-actin. CNTL, control. B, detached cells were similarly treated with the test agents, and Cav-1 S-nitrosylation was determined by immunoprecipitation using anti-Cav-1 antibody followed by Western blot analysis of the immunoprecipitated protein using anti-S-nitrosocysteine antibody. Densitometry was performed to determine the relative S-nitrosocysteine/β-actin levels. C, Cav-1 S-nitrosylation was determined by fluorometry. Immunoprecipitates from above were incubated with 200 μm HgCl2 and 200 μm diaminonaphthalene in phosphate-buffered saline. NO released from S-nitrosylated Cav-1 was quantified at 375/450 nm. Plots are the mean ± S.D. (n = 3). *, p < 0.05 versus non-treated control; #, p < 0.05 versus the indicated treatment controls.