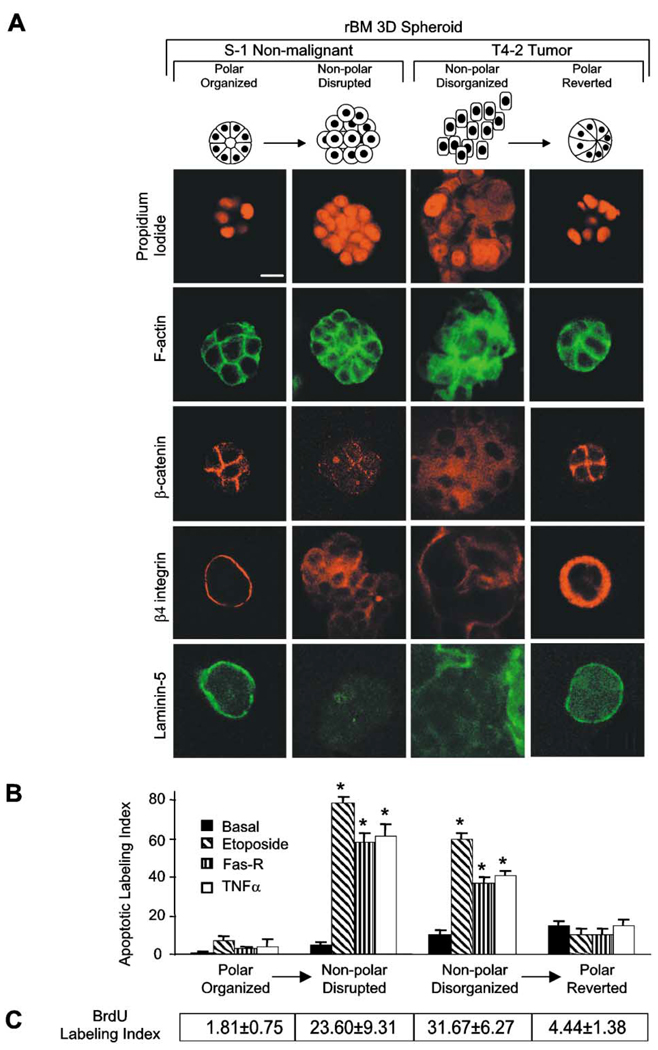
Figure 2. Polarized mammary structures are resistant to apoptosis induction.
S−1 acini produced within rBM were treated with E-cadherin function-blocking mAb (HECD-1; 25 µg/ml rBM) to perturb polarity. T4-2 structures within rBM were treated with β1 integrin inhibitory mAb (clone AIIB2; 1:50 ascites/ml rBM) to restore polarity. A: Confocal microscopy of nuclei (propidium iodide), F-actin (FITC-phalloidin), β-catenin (Texas red), β4 integrin (Texas red), and laminin-5 (FITC) fluorescence. Note that S−1 and reverted T4-2 acini exhibit cortically organized filamentous F-actin, cell-cell junction-localized β-catenin, basally localized β4 integrins, and basally secreted laminin-5. Contrast with the S−1 disrupted and T4-2 disorganized structures. B: Apoptotic labeling indices calculated for cells grown as described in A, and treated with TNF-α (100 nM), etoposide (50 µM), or anti-FAS mAb (2 µg/ml) for 96 hr. Results are mean ± SEM of 3–5 separate experiments, each with duplicates or triplicates. C: BrdU labeling indices under conditions described in B. Results are mean ± SEM of three separate experiments of 200–400 cells per experiment. All cultures were analyzed after 10 days inside the rBM. Bar equals 10 µm.