Figure 1. HGF-secreting mammary fibroblasts increase invasive outgrowths from DCIS 3D structures and their invasion through rBM.
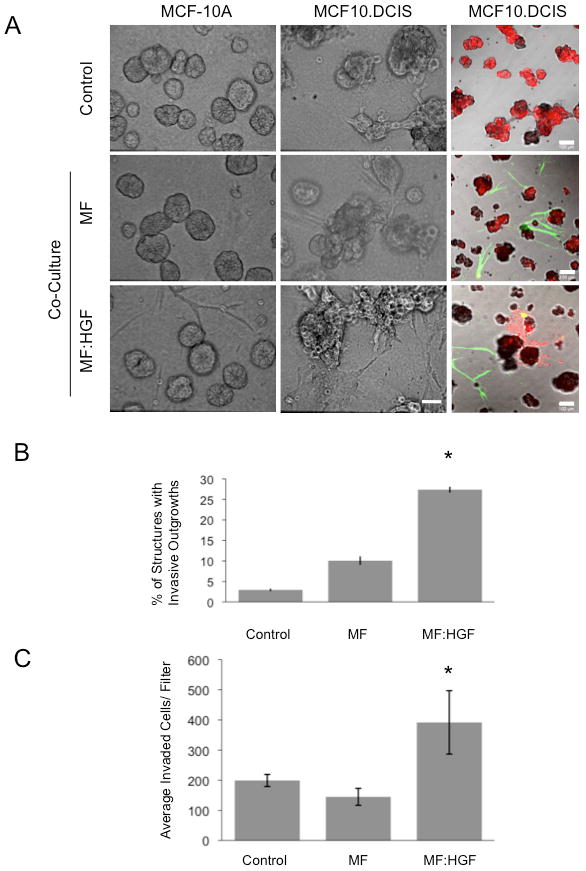
MCF-10A and MCF10.DCIS cells were grown in 3D rBM overlay culture in the absence (Control) or presence of mammary fibroblasts (MF) or HGF-secreting mammary fibroblasts (MF:HGF). A, Representative DIC images are illustrated in the 1st and 2nd column (bar, 50 μm) and representative merged images of green, red and DIC channels are shown in the 3rd column (bar, 100 μm). MCF10.DCIS cells were prelabeled with CellTracker Orange (red); fibroblasts were prelabeled with CellTracker Green (green) and embedded within the rBM. B, Images of MCF10.DCIS cells alone and in co-culture with fibroblasts were scored for the number of total structures and those with invasive outgrowths. Data in graphs are pooled from 14 fields of view in three independent experiments and are presented as the mean percentage of 3D structures with invasive outgrowths ± SD. *, p<0.02, (Student's t-test). C, Transwell invasion assay without fibroblasts (Control) or with fibroblasts grown in the well below the rBM-coated Transwell filter. Data in graphs are average number of cells that invaded through rBM coated Transwell filters, pooled from three independent experiments, and presented as mean ± SD. *, p<0.02, (Student's t-test).
