Figure 5.
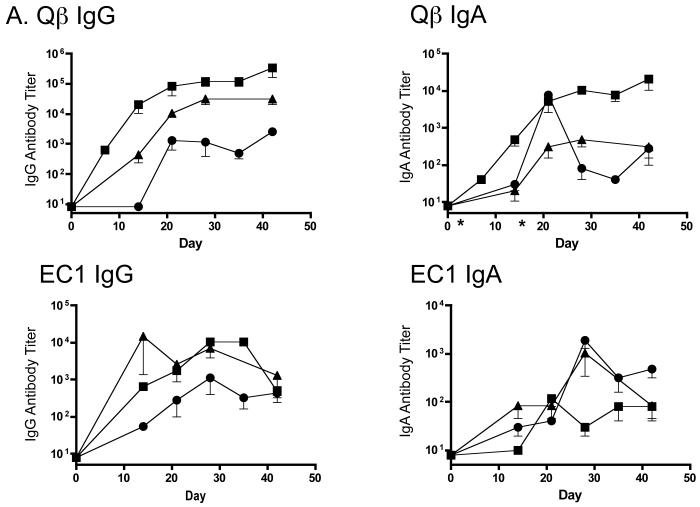
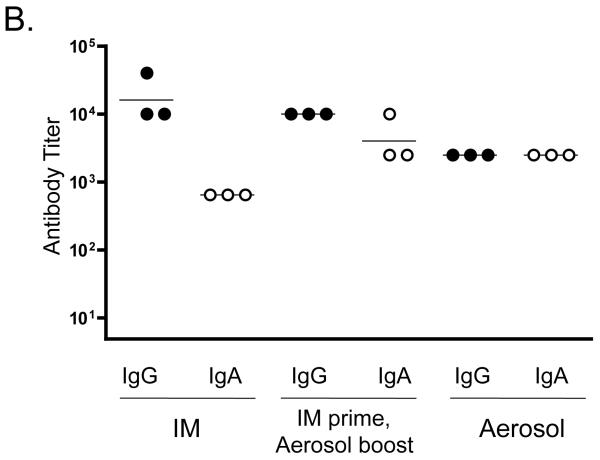
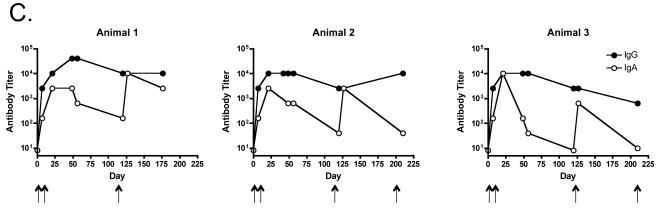
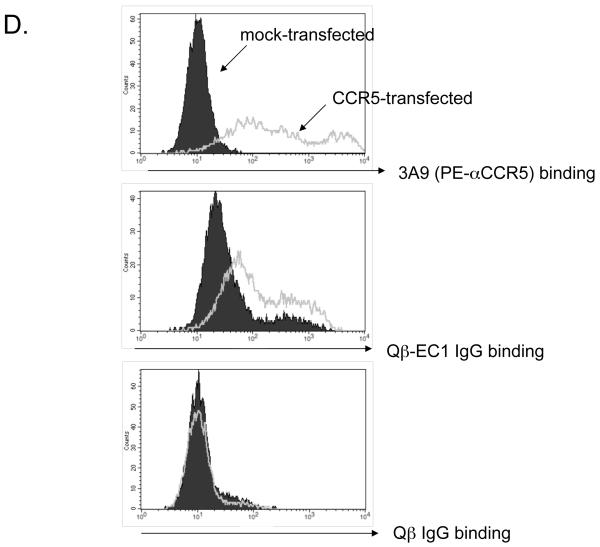
Systemic IgG and IgA responses in rats immunized with Qβ-EC1 VLPs. A) Groups of three rats were immunized intramuscularly (squares) or via the pulmonary route with (triangles) or without (circles) CTB adjuvant. Immunizations were carried out on days 0 and 14, sera were collected at the time points indicated, and antibody levels were determined by end-point dilution ELISA. Shown in the top panel are anti-Qβ IgG (left) and anti-Qβ IgA (right) antibody titers, and on the bottom panel anti-EC1 IgG (left) and anti-EC1 IgA (right) antibody titers. The data shows the geometric mean titer of three immunized rats and error bars represent SEM. B) Comparison of IgG and IgA serum anti-EC1 titers in rats one week following a second inoculation with Qβ-EC1. Rats received two intramuscular inoculations, two inoculations via aerosol, or an intramuscular prime followed by an aerosol boost. C) Kinetics of serum anti-EC1 responses in individual rats receiving an IM prime followed by aerosol boosts of Qβ-EC1. Rats were immunized on weeks 0, 2, 6, and 15 (arrows), sera collected at the time points indicated and IgG (closed circles) and IgA (open circles) titers were determined by ELISA. D) Immunization of rats via pulmonary route induces antibodies that bind native CCR5. 293T cells were mock-transfected (filled) or transfected with an expression vector encoding pig-tailed macaque CCR5 (line). Two days after transfection, cells were incubated with a PE-labeled monoclonal antibody 3A9 (top), pooled protein G-purified IgG from Qβ-EC1 immunized rats (middle), and pooled protein G-purified IgG from Qβ-immunized rats (bottom), and then antibody binding was assessed by flow cytometry.