Figure 4.
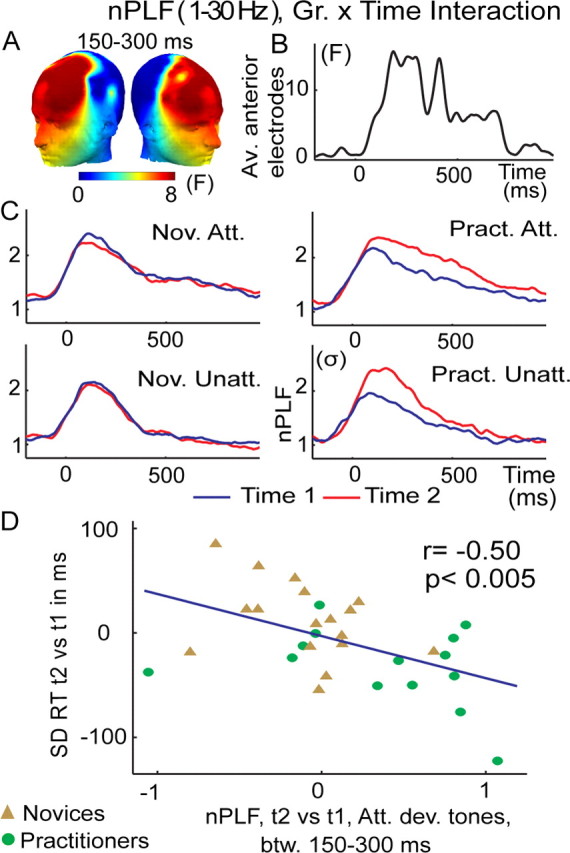
Intensive mental training increases trial-to-trial consistency of brain responses to any deviant tones. A–D, The graphs show the group × time interaction on broadband (1–30 Hz) nPLF following the display conventions and analysis from Figure 2. A mental training-related increase in phase locking to deviant tones in general (attended and unattended) was significant (p < 0.05, corrected) between 150 and 300 ms across the a priori group of frontal electrodes (A–C) and correlated negatively, for the attended deviant tones, with the observed reduction in RT SD (D). A similar negative correlation (r = −0.30) was found for the unattended deviant tones, even if this effect did not reach significance (p = 0.11).
