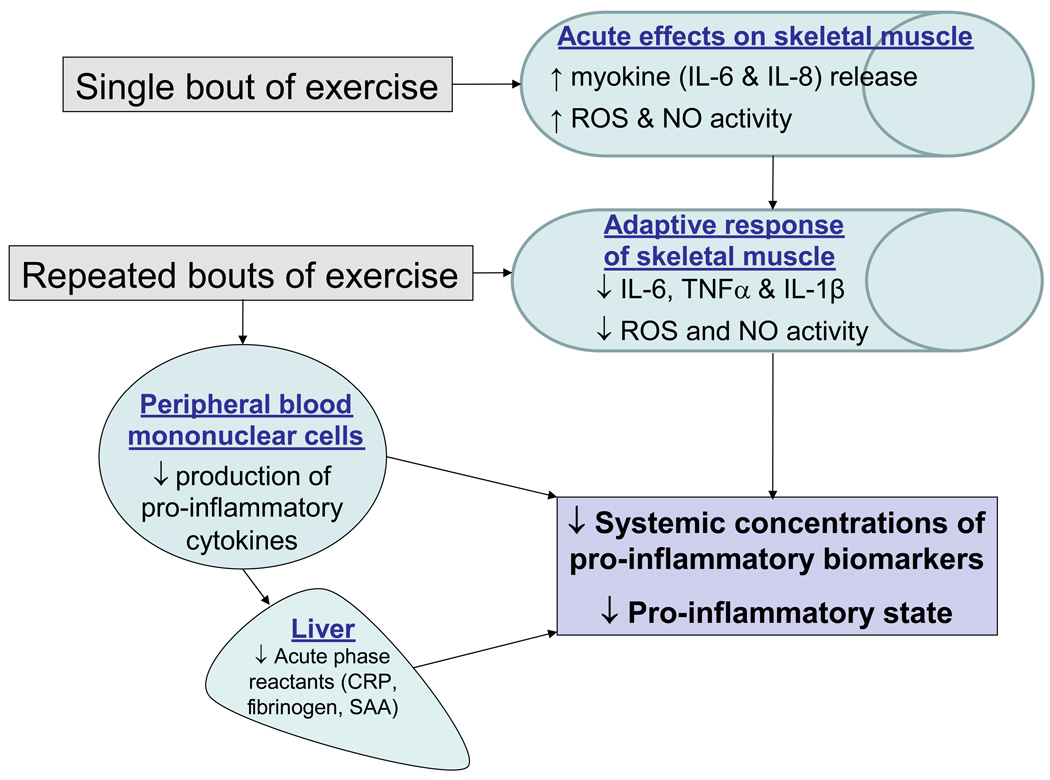
Figure 2.
Schematic of adaptations to exercise training potentially underlying improvements in chronic inflammation. Adaptive responses in inflammatory and redox-sensitive pathways in skeletal muscle, as well as potential adaptive responses in innate immune cells, may serve to protect against chronic systemic low-grade inflammation.
CRP=C Reactive protein, SAA=serum amyloid a, ROS=reactive oxygen species; NO=nitric oxide