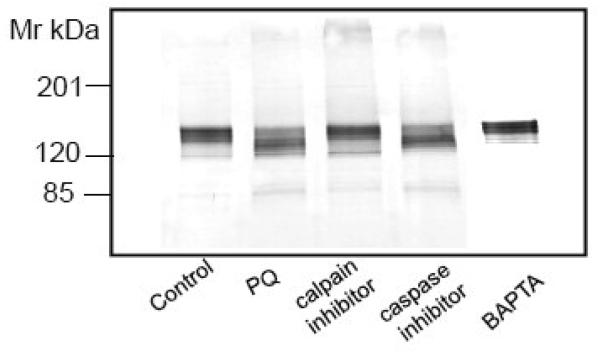
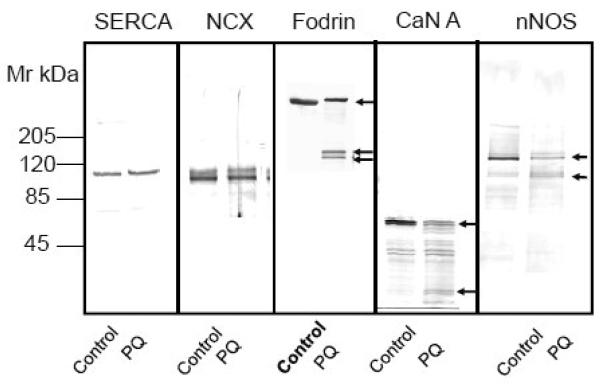
Fig. 7.
Effect of calpain and caspase inhibitors and a Ca2+ - chelating agent on PQ - induced PMCA proteolysis and degradation of other known calpain substrates. (A) Neurons were exposed to 50 μM PQ for 24 h in absence and presence of a calpain specific inhibitor (carbobenzoxy-valyl-phenylalaninal, 100 μM), or a pan caspase inhibitor (benzyloxycarbonylval-ala-asp-fluoromethyl ketone, 100 μM), added to the cell culture media 1h prior to PQ. Chelation of [Ca2+]i was accomplished by replacing the cell culture medium with a Ca2+-free medium and exposing neurons to BAPTA-AM (50 μM) for 30 min. Ten microgram of protein from the particulate fraction was immunoblotted and probed with pan PMCA antibody (1:1000). (B) Effect of PQ on other known calpain substrates. Neuronal lysate (30 μg) was run on SDS-PAGE (4-12% gradient gel), transferred, and probed with antibodies to two other Ca2+ transporters that are not regulated by CaM, i.e., SERCA (1:500) and NCX (1:500), and to three proteins that are regulated by CaM, i.e., α-fodrin (1:1000), CaN A (1:500), and nNOS (1:1000). Representative blots from 3 independent experiments with similar results are shown.