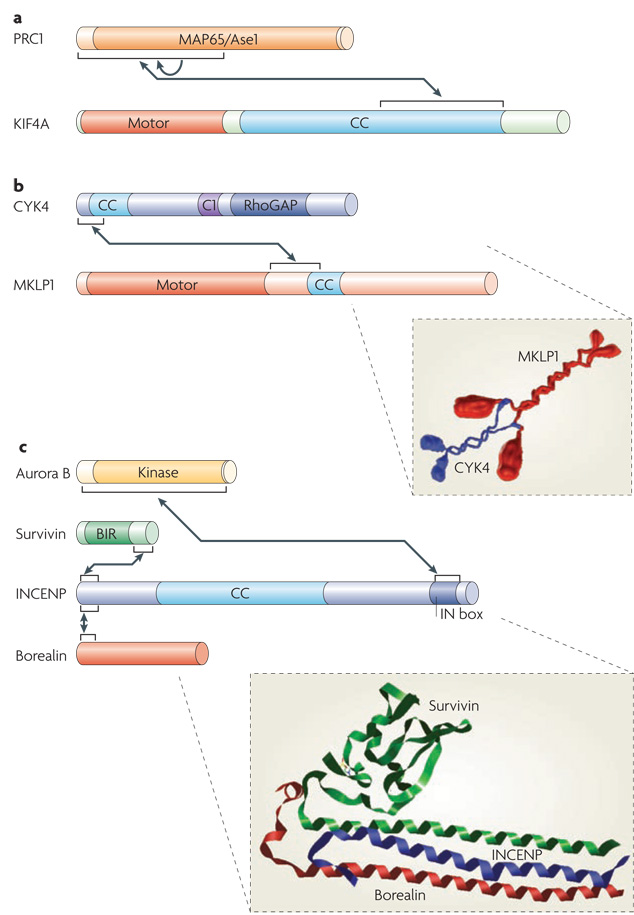
Figure 2. Structural features of central spindle components.
Box diagrams of featured central spindle components. Arrows indicate established protein-protein interactions. a| Protein regulating cytokinesis 1 (PRC1) contains a large central conserved domain ( MAP65/Ase1) that interacts with microtubules. The kinesin-4 motor KIF4 contains an N-terminal motor domain and a large coiled-coil region (CC). The N terminus of PRC1 is required for dimerization (indicated by the arrow) and for interacting with KIF4. b|Centralspindlin is a heterotetramer assembled from the Rho family GTPase activating protein (GAP) CYK4 and mitotic kinesin-like protein 1 (MKLP1) dimers. CYK4 consists of N-terminal coiled-coil, central C1 and C-terminal RhoGAP domains. MKLP1 consists of an N-terminal motor domain, an extended neck linker region and a short coiled-coil region. Both CYK4 and MKLP1 form parallel coiled-coils. Assembly of CYK4 and MKLP1 into centralspindlin is mediated by the N terminus of CYK4 binding to the neck linker region of MKLP1 (see inset). c| The chromosome passenger complex (CPC) is a heterotetramer comprised of Aurora B, survivin, INCENP and borealin. The N-terminal regions of survivin, borealin and INCENP form a three helical bundle. The BIR (Baculoviral inhibition of apoptosis protein repeat) domain of survivin is required for localization to the inner centromere but not the central spindle. The C-terminal IN box of INCENP binds to the kinase domain of Aurora B. Also shown is a structural model of the interacting regions of survivin-borealin-INCENP core complex (see inset) (http://dx.doi.org/10.2210/pdb2qfa/pdb). Protein box diagrams are drawn to scale.