Figure 1.
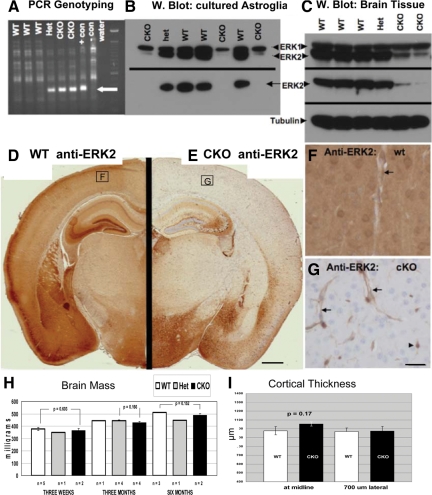
Conditional deletion of ERK2 from the CNS via Nestin:Cre-mediated recombination. A: PCR assay for recombination at the floxed ERK2 locus. DNA extracted from the cerebellum of 3-week-old littermates was amplified using primers flanking ERK2 exon 2. A 350-bp product, indicating loxP-directed deletion of the allele, is detected in both heterozgous (Het) and homozygous knockouts (CKO), as well as in a positive control sample (ERK2fl/fl astrocytes infected with Adeno-Cre (+con)). B: Western blot reveals ERK2 protein loss from cultured neonatal astrocytes. Total ERK1/2 (upper panel) blotting reveals selective loss of ERK2, but not ERK1, in cKO cells. An ERK2-specific antibody (lower panel) demonstrates complete loss of ERK2 in cKO cells. C: Western blotting of brain tissue from 3-week-old littermates reveals selective reduction of ERK2 in cKO mice, with no apparent compensatory ERK1 up-regulation. D–G: Immunohistochemical demonstration of loss of ERK2 immunoreactivity in ERK2 cKO cortex. Coronal sections of 3-week-old littermates (taken 1.80 mm caudal to Bregma) were stained in parallel using an ERK2-specific antibody. Whereas wild-type (WT) cortex exhibits intense ERK2 immunostaining in cortical neurons and neuropil (D), cKO mice show complete loss of cortical neuropil immunoreactivity (E). Some brain regions, including hippocampal CA2/3 and hypothalamus, consistently show retention of some ERK2 immunoreactivity (E). Higher power images of cortical ERK2 staining (corresponding to the boxed regions in D and E) reveal neuronal, neuropil, and vascular staining in the WT (F). As expected from a Nestin:Cre-driven recombination, neuronal and neuropil ERK2 is eliminated in the cKO cortex, whereas endothelial (arrows) and probable microglial (arrowhead) expression is retained (G). Neither brain mass (H) nor frontal cerebral cortex thickness (I) is affected in ERK2 cKO mice. Scale bar in G represents 25 μm, applies to F and G.