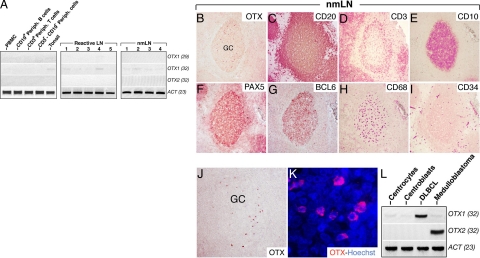
Figure 3.
OTX1 expression in normal lymphoid cell populations, reactive LNs, and nmLNs. A: OTX1 expression analysis in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC), CD19+ peripheral B-cells, CD3+ peripheral T-cells, CD3−/CD19− peripheral lymphocytes, total tonsil tissue, five LNs with reactive follicular hyperplasia (reactive LN), and four nmLNs shows a faint signal only at 32 PCR cycles in tonsil, reactive LNs, and nmLNs, while no signal is detected for OTX2 in all of the samples. Immunodetection of OTX1 (B and J), CD20 (C), CD3 (D), CD10 (E), PAX5 (F), BCL6 (G), CD68 (H), and CD34 (I) by using carbazole staining in adjacent sections of a nmLN shows that, according to the gross distribution of GC cell-markers, a few OTX1+ cells are detected only in the GC area. K: OTX immunohistochemistry in Hoechst-stained GC cells shows that OTX1 is prevalently localized to the cytoplasm. L: OTX1 and OTX2 RT-PCR show a very low level of OTX1 transcripts in both CCs and CBs while no expression for OTX2 is detected. As a positive control, the expression of OTX1 and OTX2 is shown in DLBCL and medulloblastoma, respectively. GC, germinal center.