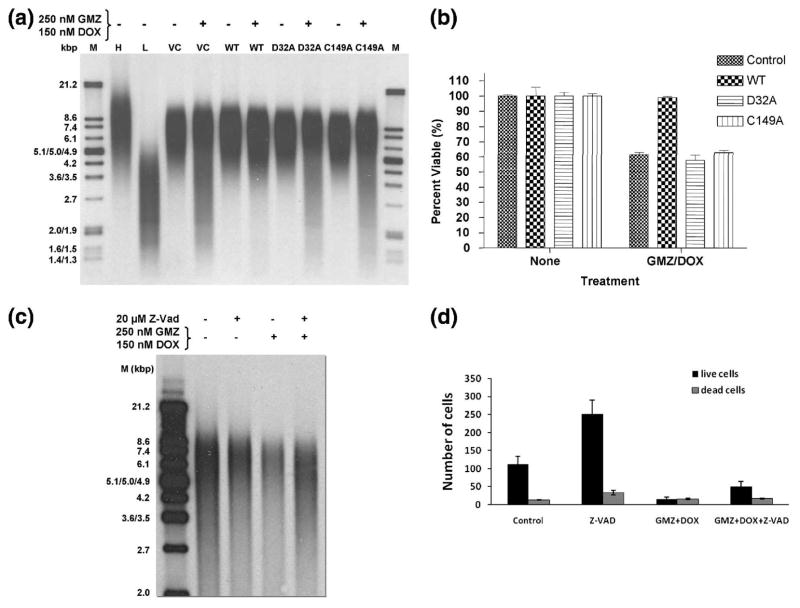
Fig 9.
A549 cells transfected with D32A or C149A mutants of GAPDH are no longer protected against treatment by GMZ and DOX. (A). A549 cells were transfected with vector control (VC), WT, D32A or C149A constructs and telomeric restriction fragment lengths were analyzed after 48 hours treatment with 250 nM GMZ and 150 nM DOX. M= markers; H= high molecular weight markers; L= low molecular weight markers. (B). Cell viability was measured using an MTT assay in which untransfected cells (control), or cells transfected with constructs expressing WT, D32A or C149A GAPDH, were treated with 250 nM GMZ and 150 nM DOX. Percent viability was calculated from the differences in absorbance of treated vs. untreated cells. Data were analyzed using 2-way ANOVA (p<0.001) (n=3). (C). Telomere length of A549 cells treated with GMZ/DOX in the presence or absence of Z-VAD (20 μM) was analyzed as described in (A), and the results were compared to untreated controls. (D). Effects of GMZ/DOX on cell survival or death were determined using trypan blue exclusion assay. Error bars represent standard deviations.