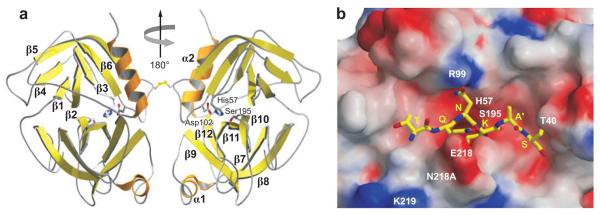
Figure 2.
Crystal structure of the GzmA homodimer. (a) GzmA is a disulfide-linked dimer in which the two active sites, indicated on the right (His57-Asp102-Ser195), face in opposite directions. The surface of the molecule contains concentrations of basic amino acids, which may explain the preference for acidic protein substrates through binding outside the active site through an extended exosite. (b) The SET protein is an important target of GzmA, whose cleavage triggers its unique pathway of DNA damage. Model of how the SET peptide surrounding the GzmA cleavage site fits into the GzmA active site. [Figures based on the structure obtained by Hink-Shauer and colleagues (54a), reprinted with permission.]