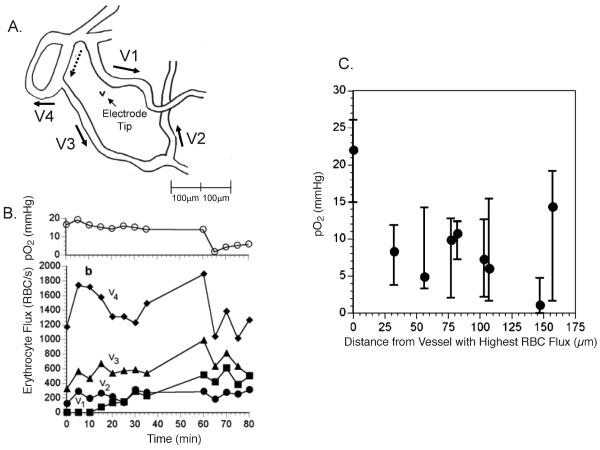
FIG. 1.
Relationship between red cell flux variation and interstitial pO2 in a skin fold window chamber tumor. Panel A: Tracing of vascular field, taken from a video monitor, indicating direction of flow for segments surrounding an interstitial location for pO2 measurement. Panel B: Time tracings of red cell flux and interstitial pO2 for an 80-min observation period. Note that the interstitial pO2 drops toward the end of the period, commensurate with a reduction in red cell flux. Panel C: Summary figure from several experiments showing the median and magnitude of fluctuations in pO2 as a function of distance from the microvessel in each preparation with the highest red cell flux. These data strongly suggest that cycling hypoxia can exist near the diffusion limit of oxygen. Oxygen tension measurements were made using recessed tip oxygen microelectrodes with tip diameters <10 μm. Figure adapted from Lanzen et al. with permission from the author and publisher (34).