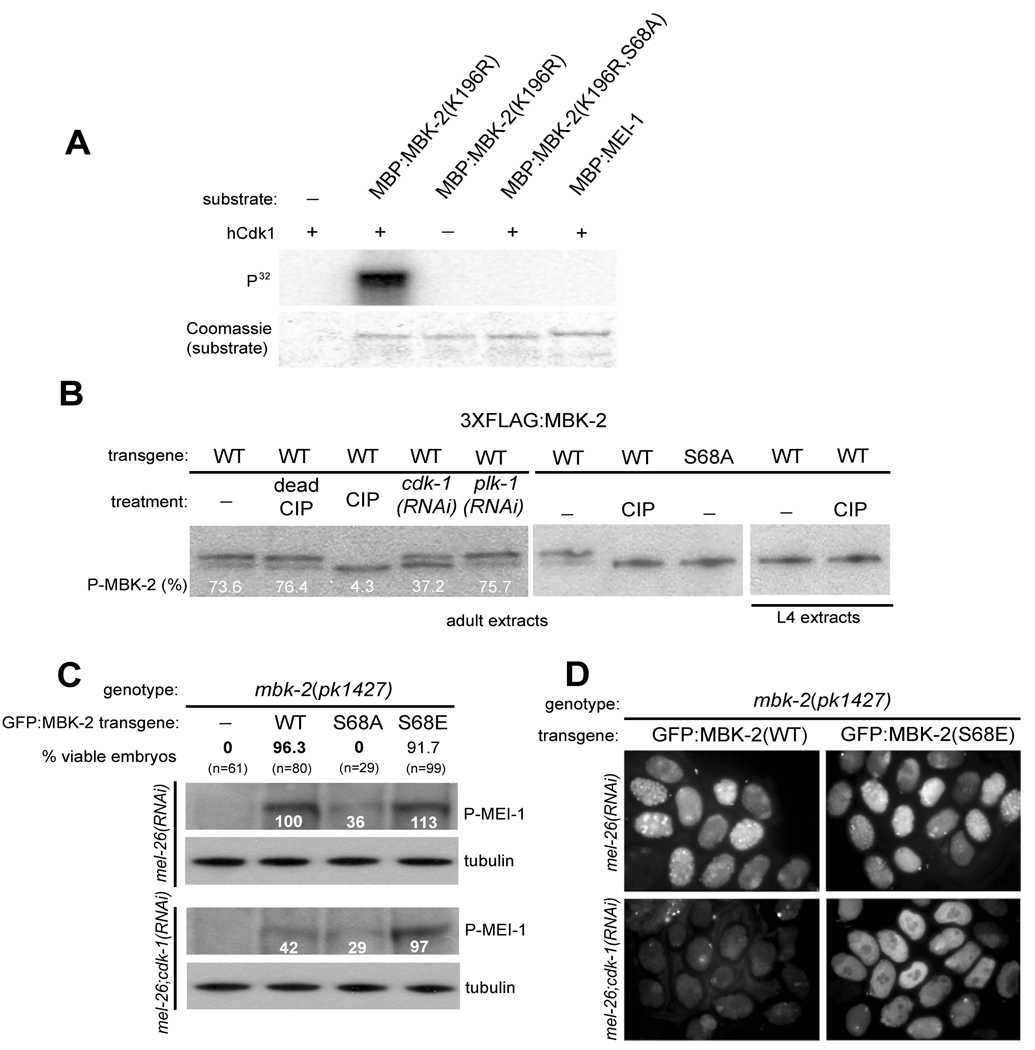
Fig. 2. MBK-2 is activated by CDK-1.
(A) hCdk1 phosphorylates MBK-2.
hCdk1 (New England Biolabs) was incubated with the indicated maltose-binding fusions (partially purified from E. coli) in the presence of γ-32P-ATP. Coomassie staining controls for loading of MBP fusions. We estimate that 43% of MBP:MBK-2 was phosphorylated in this assay. MBK-2(K196R) is a mutation in the ATP binding domain of MBK-2 (Sup. Fig. 1) that eliminates MBK-2’s own kinase activity (Stitzel et al., 2006).
(B) FLAG-tagged MBK-2 was immunoprecipitated from adults (hermaphrodites with 4 or more embryos) or L4 (late L4/early adults with 0–1 embryo in uterus) whole worm extracts, treated with Calf Intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase (CIP), and western blotted with anti-FLAG antibody. Numbers represent the percent of phosphorylated FLAG:MBK-2 compared to total FLAG:MBK-2.
(C) mbk-2(pk1427) hermaphrodites transformed with the indicated transgenes were 1) tested for rescue of maternal-effect lethality (% viable embryos, N= number of embryos scored) and 2) western blotted for phospho-MEI-1. Numbers underneath the phospho-MEI-1 bands indicate relative intensity with respect to that observed in mbk-2(pk1427) hermaphrodites expressing wild-type MBK-2 (set to 100%). mel-26(RNAi) is used to stabilize phospho-MEI-1. Note that cdk-1(RNAi) reduces the level of phospho-MEI-1 significantly only in hermaphrodites carrying the wild-type transgene (100 vs 42).
(D) Immunofluorescence using the anti-phospho-MEI-1 antibody on embryos derived from hermaphrodites of indicated genotype. Note that cdk-1(RNAi) eliminates staining in embryos from mothers expressing the wild-type MBK-2 transgene, but not from mothers expressing the MBK-2(S68E) transgene.