Fig. 5. EGG-4/5 interact with MBK-2 in vivo and in vitro.
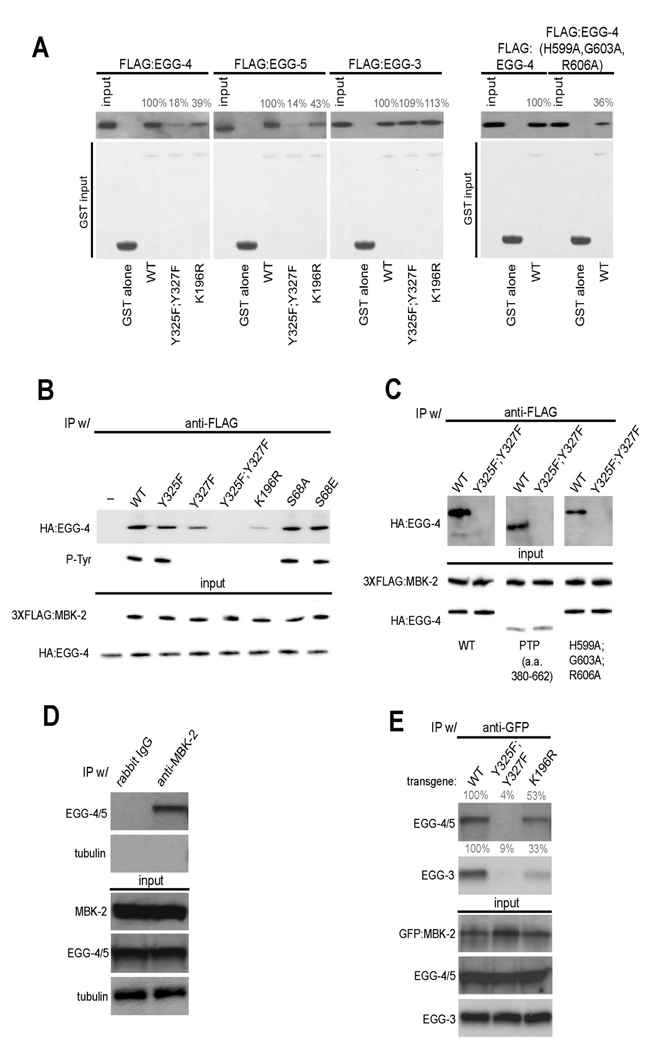
(A) EGG-4/5 bind to MBK-2 in vitro. Extracts from E. coli expressing the indicated FLAG:EGG fusions were pulled down with the indicated GST:MBK-2 fusions and immunoblotted with an anti-FLAG antibody. Numbers (%) indicate signal intensity relative to wild-type. Input is 1/50th of the pull-down. EGG-4(H599A,G603A, R606A) has mutations in consensus residues in the predicted phosphatase catalytic site (see Sup. Fig. 5).
(B) EGG-4 interacts with MBK-2 in mammalian cells. HA-tagged EGG-4 and FLAG-tagged MBK-2 were co-expressed in HEK293 cells, immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG, and probed with an anti-phosphotyrosine antibody and an anti-HA antibody. Input is 1/100 of the IP.
(C) EGG-4 uses its protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) domain to interact with MBK-2. HA and FLAG tagged proteins were co-expressed and immunoprecipitated as in (B). EGG-4(380–662) is the PTP domain (see Sup. Fig. 5). Input is 1/100 of the IP.
(D) EGG-4/5 and MBK-2 interact in worm extracts. Anti-MBK-2 immunoprecipitates from whole worm extracts were western blotted with anti-EGG-4/5 antibody and anti-tubulin antibody (negative control). Input is 1/100th of the IP. Rabbit IgG is a negative control antibody.
(E) The EGG-4/5/MBK-2 interaction requires the MBK-2 activation loop in vivo. Anti-GFP immunoprecipitates from whole worm extracts were western blotted with anti-EGG-4/5 and anti-EGG-3 antibodies. Anti-GFP pulls down endogenous EGG-4/5 and EGG-3 from worms expressing wild-type GFP:MBK-2 or GFP:MBK-2(K196R) (kinase dead), but not from worms expressing GFP:MBK-2(Y325F,Y327F) (activation loop mutant). Numbers (%) indicate signal intensity relative to wild-type. Input is 1/100th of the IP.
