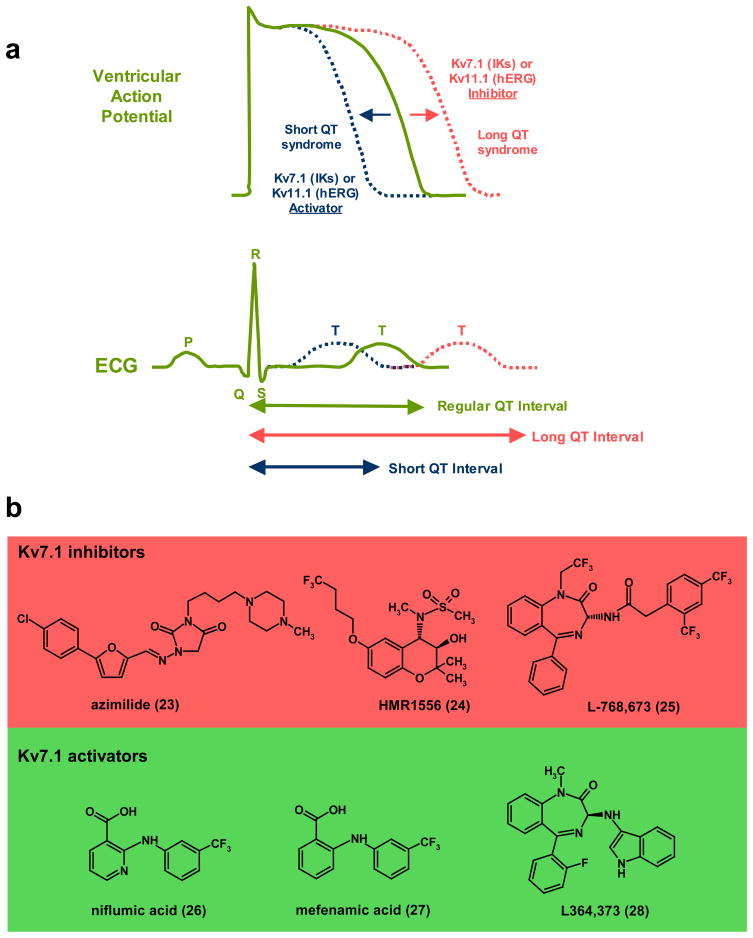
Figure 4. KV7.1 and KV11.1 are crucial for determining the length of the cardiac action potential.
a, Illustration of ventricular action potential (AP) and electrocardiogram (ECG) showing effects of Long- and Short-QT syndrome as well as pharmacological modulators of KV7.1 (IKs) or KV11.1 (hERG) on AP duration and length of QT interval. Inhibition of KV7.1 and KV11.1 produces prolongation of ventricular AP duration which is similar to what occurs in acquired or hereditary Long QT syndrome. Activators of KV7.1 or KV11.1 reduce the duration of cardiac action potential which is manifested as a shorter QT interval b, KV7.1 inhibitors: (23), azimilide (Procter & Gamble)128,129; (24), HMR1556 (Sanofi-Aventis)134; (25), L768,673 (Merck)138. Azimilide has been shown to reduce atrial fibrillation (AF) in clinical trials128,129, while HMR1556 and L768,673 are effective in dog models of AF. KV7.1 activators: (26), niflumic acid139; (27), mefenamic acid139; (28), L384,373 (Merck)141.