Fig. 1.
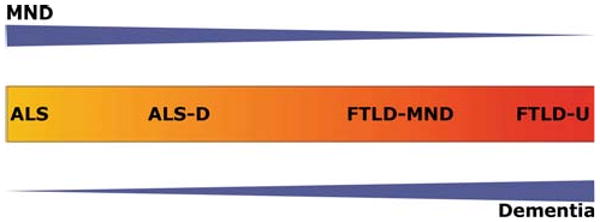
43 kDa nuclear trans-active response DNA-binding protein (TDP-43) multisystem diseases: clinico-pathological spectrum. Schematic illustration of the concept of a clinico-pathological spectrum of the major TPD-43 diseases extending from frontotemporal degeneration with ubiquitin positive, tau and α-synuclein negative inclusions (FLTD-U) at one end to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) at the other. Blue arrowhead-like triangles denote clinical syndrome with motor neuron disease decreasing and dementia increasing from left to right. Color change from yellow to red in central box denotes increasing spread and severity of TDP-43 pathology in the brain and spinal cord, as an approximate estimation. Specifically, yellow represents predominant involvement of the spinal cord and red represents predominant involvement of cortical areas. Other brain areas are not as explicitly represented in this color coded diagram. MND motor neuron disease, ALS-D ALS with dementia, FTLD-MND frontotemporal degeneration with MND
