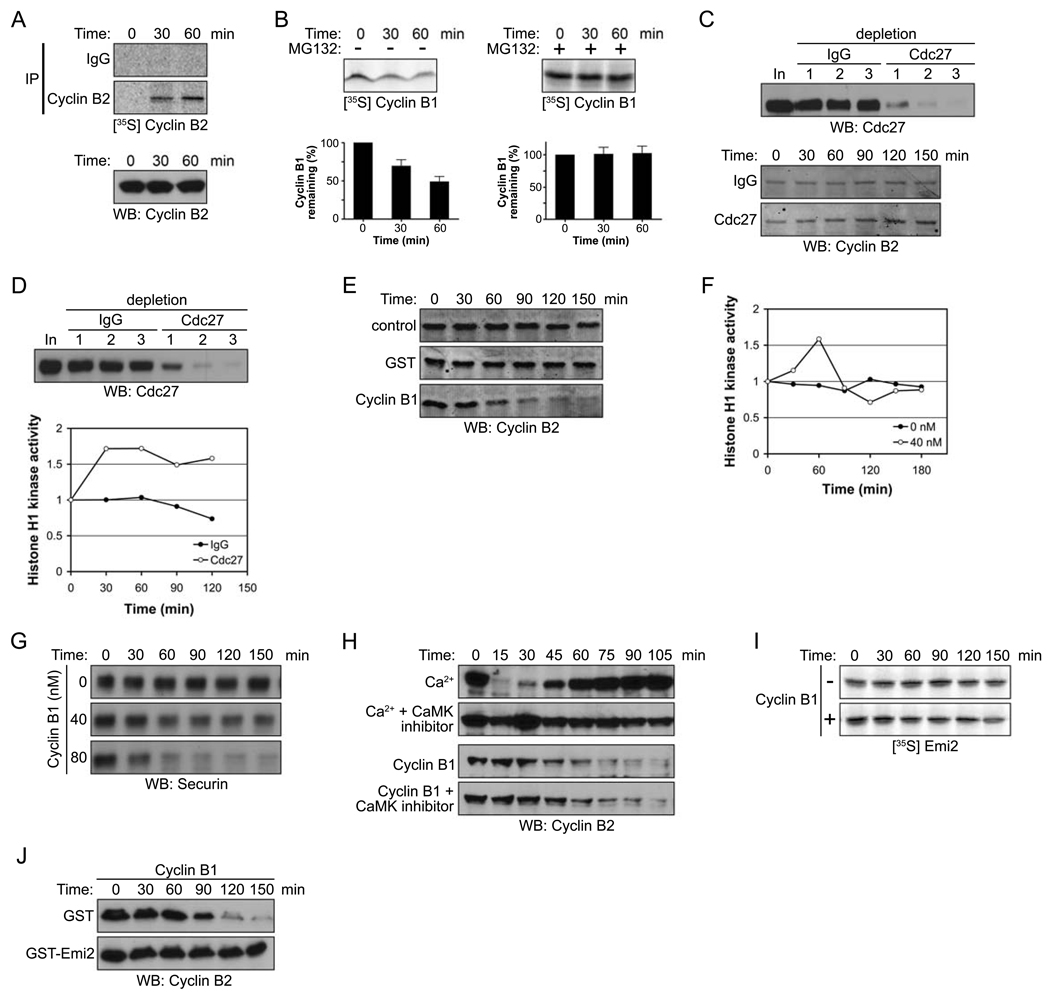
Figure 1. Emi2 antagonizes Cdc2/Cyclin B-induced degradation of Cyclin B.
(A) (Top): CSF-arrested Xenopus egg extracts were incubated in the presence of 35S-labeled methionine and cysteine. At the indicated times, endogenous Cyclin B2 protein was immunoprecipitated and newly synthesized Cyclin B2 was detected by autoradiography. (Bottom): Total Cyclin B2 levels were measured in a CSF extract at the indicated times by immunoblotting.
(B) (Top): 35S-labeled Cyclin B1 was added into CSF extracts in the absence (−, left) or the presence (+, right) of MG132 (100 µM). Aliquots were withdrawn at the indicated times and the amount of Cyclin B1 was detected by autoradiography. (Bottom): The radiolabeled Cyclin B1 remaining at each time point was quantified. Error bars represent standard deviation of four measurements.
(C) (Top): The APC was depleted from CSF extracts with three sequential incubations with IgG or Cdc27 antibodies. Samples from each extract were resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-Cdc27 antibodies. (Bottom): Samples were taken from control or APC (Cdc27) depleted extracts at the indicated times after incubation with energy regenerating mix at room temperature. The amount of Cyclin B2 was examined by immunoblotting (10 µg total protein was loaded per lane to clearly visualize the changes in endogenous Cyclin B levels).
(D) (Top) The APC was depleted from CSF extracts as described in (C). (Bottom): After 30 min incubation at room temperature, the Cdc2/Cyclin B kinase activity in control or APC (Cdc27) depleted extracts was measured at the indicated times using Histone H1 kinase assays. The phosphorylation of Histone H1 was quantified, normalized and plotted.
(E) Buffer (control), GST, or 40 nM Cyclin B1 was added to CSF extracts. At the indicated times, samples were withdrawn and endogenous Cyclin B2 levels were measured by immunoblotting.
(F) At the indicated times, Cdc2/Cyclin B kinase activity in the CSF extracts was measured in the presence or absence of recombinant Cyclin B1 (40 nM) using Histone H1 as an exogenous substrate. The phosphorylation of Histone H1 was quantitated, normalized, and plotted.
(G) Buffer (control) or Cyclin B1 (40 nM or 80 nM) was added to CSF extracts. At the indicated times, samples were withdrawn and Securin levels were measured by immunoblotting.
(H) Ca2+ or recombinant Cyclin B1 was added into CSF extracts in the presence or absence of the CaMKII peptide inhibitor (281–309, 400 µM). Samples were taken at the indicated times and the amount of endogenous Cyclin B2 was measured by immunoblotting.
(I) Radiolabeled Emi2 was added into CSF extracts supplemented with 40 nM recombinant Cyclin B1. The levels of Emi2 in the extract were examined at the indicated times by autoradiography.
(J) Cyclin B1 was added into CSF extracts in the presence of GST or GST-Emi2. At the indicated times, samples were taken and the amount of endogenous Cyclin B2 was determined by immunoblotting.