Fig. 1.
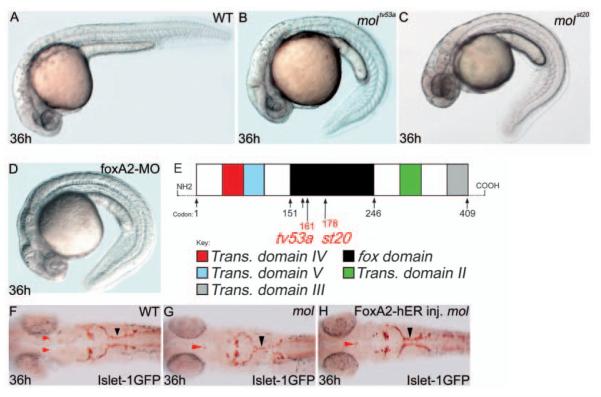
The mol locus encodes Foxa2. (A-D) Lateral views of 36 hpf wild-type (A), moltv53a (B), molst20 (C) and foxa2 morphant (D) embryos. (E) Structure of the Foxa2 protein showing the positions of the likely truncations within the forkhead domain caused by the moltv53a and molst20 mutations. moltv53a results in the complete loss of transactivating domains II and III, leaving a C-terminally truncated Foxa2 protein. molst20 disrupts the forkhead box DNA-binding domain, downstream of moltv53a. Trans. domain, transactivating domain; fox domain, forkhead box DNA-binding domain. (F-H) Dorsal views of brains of a wild-type (F) and two moltv53a mutant (G,H) embryos labelled to reveal the cranial motor nuclei. The fusion of the facial motor nucleus (black arrowheads) is rescued in the moltv53a embryo expressing functional Foxa2 (H). The embryo in H is a homozygous moltv53a mutant as it still shows midline fusion of a reduced oculomotor nucleus (red arrowhead).