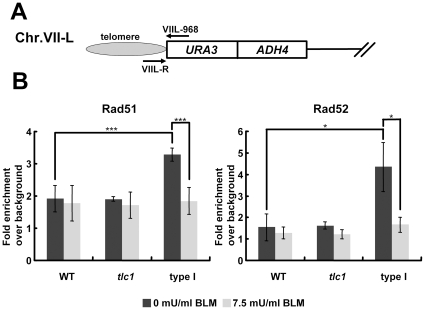
Figure 5. Sequestration of repair proteins at telomeres in type I survivors.
(A) The left arm of chromosome VII-L in YPH499 UT strain was modified by integration of fragments containing the URA3 and telomeric sequence at the ADH4 locus. Telomeres are represented by hatched ovals; arrows indicate primers used for real-time PCR. (B) ChIPs were performed and quantitated by real-time PCR as described in Materials and Methods. Error bars represent standard deviations for at least three independent experiments. Before the addition of bleomycin (black bars), bindings of Rad51 and Rad52 to the VII-L telomere in type I cells differed from those in wild-type in a statistically significant manner (P values = 5.36×10−8 and 0.010, respectively), and their bindings to the VII-L telomere was statistically indistinguishable in pre-senescent tlc1 mutant and wild-type strains. In type I cells, bindings of Rad51 and Rad52 to the VII-L telomere before bleomycin treatment (black bars) differed from those after treatment (gray bars) in a statistically significant manner (P values = 0.0004 and 0.014, respectively). This discrepancy was not observed in both pre-senescent tlc1 mutant and wild-type strains.