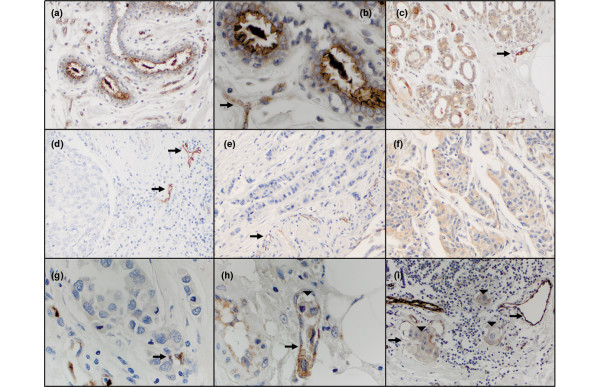
Figure 6.
MUC4 expression in human breast tissue. Tissue microarrays were analyzed by immunohistochemistry using 1G8s. (a) Normal human breast of patient number 1 at 200×. (b) High magnification (500×) of patient number 1 normal breast, highlighting strong apical staining of MUC4 in epithelia, and endothelial staining (black arrow) as an internal control. (c) Normal human breast tissue of patient number 2 at 200×, exhibiting cytoplasmic staining patterns. (d) Matched primary invasive ductal carcinoma (200×) of patient number 2. Note the MUC4-positive blood vessels (black arrows), but the neoplastic epithelial cells are negative. (e) Primary invasive ductal carcinoma (200×) of patient number 3 with positive endothelial cells noted as black arrows, but no detectable neoplastic epithelial cell staining. (f) Matched metastatic breast carcinoma of the lymph node of patient number 3. Note increased staining intensity of MUC4. (g) Primary invasive ductal carcinoma (500×) of patient number 4 with many mitotic figures. (h) Matched metastatic tissue from patient number 4 showing a tumor embolus (500×, arrowhead). Note the MUC4-positive tumor cells within the lymphovascular space. (i) Metastatic breast tumor of patient number 5 (200×). Note the lymphocytes and intensely positive vessels (black arrows). Three tumor emboli are noted (arrowheads).