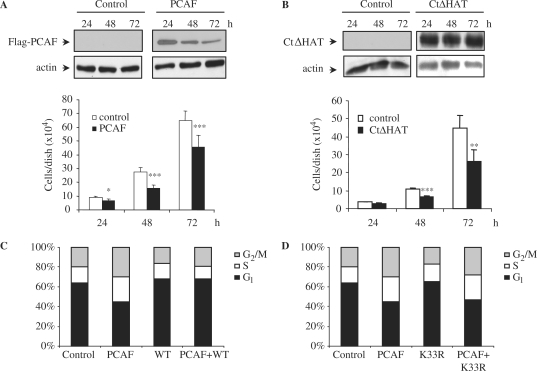
Figure 5.
PCAF impairs cell proliferation by causing S and G2/M cell cycle arrest. (A) NIH3T3 cells were transfected with empty vector or Flag-PCAF, then counted, and equal amounts were seeded in triplicates in 6-well-plates. Cell proliferation was measured by counting the number of cells present in each well 24, 48 and 72 h after transfection. Results shown are the mean of three independent experiments ± SE. *P-value <0.05; **P-value <0.01; ***P-value <0.001. A WB showing the levels of transfected PCAF is shown in the top panel, and a WB with anti-actin was performed as a loading control (bottom panel). (B) Similar experiments as in (A) were performed using a NIH3T3 clone expressing CtΔHAT-PCAF under a Tet-off system generated as described in the ‘Materials and Methods’ section. Equal amounts of cells were seeded in triplicates in 6 well plates. Cell proliferation was measured by counting the number of cells present in each well 24, 48 and 72 h after seeding. CtΔHAT expressing cells were cultured in the absence of tetracyclin. As a control, the same clone was cultured in medium supplemented with tetracyclin. Results shown are the mean of three independent experiments ± SE. *P-value <0.05; **P-value <0.01; ***P-value <0.001. A WB showing the levels of CtΔHAT-PCAF is shown in the top panel, and a WB with anti-actin was performed as a loading control (bottom panel). (C) HCT-116 cells were transfected with YFP-PCAF, CFP-cdk2WT or both. At 48 h after transfection they were fixed, DNA was stained with TOPRO-3 and transfected cells were analysed by FACS. The percentage of cells in each phase of the cell cycle is represented in the graph. (D) The same as in (C), but in this case cells were transfected with YFP-PCAF, CFP-cdk2 K33R, or both.