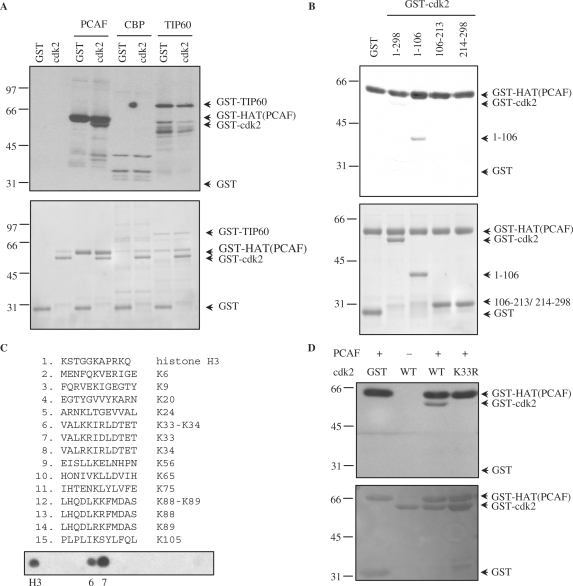
Figure 6.
Cdk2 is a substrate acetylated by PCAF in vitro. (A) Purified GST-cdk2 was subjected to in vitro acetylation assays using the catalytic domain of PCAF [GST-HAT(PCAF)], GST-CBP or GST-Tip60 in the presence of [14C]acetylCoA. Purified GST was used as a negative control substrate. In the assays with PCAF or Tip60 their autoacetylation was used as a positive control, whereas in the case of CBP, histones were used as a positive control substrate (see Supplementary Data Figure S4A). Acetylated proteins were visualized by autoradiography (top panel). A loading control gel was stained with coomassie blue (bottom panel). (B) Purified recombinant cdk2 fragments were subjected to in vitro acetylation assays as in (A) using GST-HAT (PCAF) as acetylase. Acetylated proteins were visualized by autoradiography (top panel). A loading control gel was stained with coomassie blue (bottom panel). (C) Fourteen peptides including one or two consecutive lysines from the cdk2 fragment including aa 1–106, were spotted on a membrane. As a positive control a peptide from histone H3 was added. The membrane was subjected to in vitro acetylation assays with GST-HAT(PCAF) and [14C]acetylCoA. Acetylation was visualized by autoradiography. (D) Purified GST-cdk2 WT and GST-cdk2 K33R were subjected to in vitro acetylation assays with GST-HAT(PCAF). Acetylation was visualized by autoradiography (top panel). A loading control gel was stained with red ponceau (bottom panel).