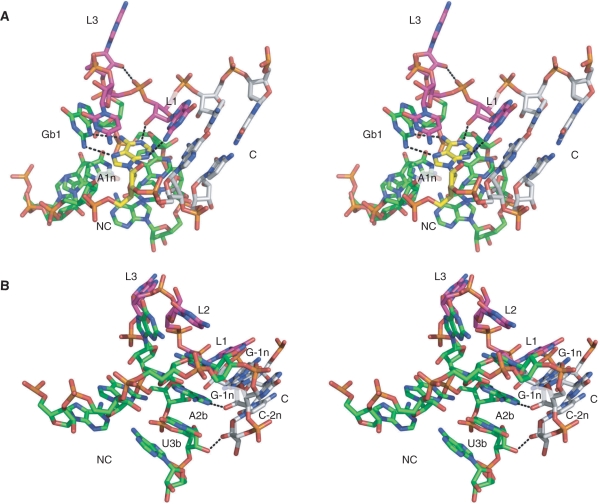
Figure 5.
Hydrogen bonding in the Kt-23 k-turn. Parallel-eye stereoscopic views of the structure of Kt-23 taken from the crystal structure of the T. thermophilus 30S ribosomal subunit, with key hydrogen bonds indicated by broken lines. (A) Hydrogen bonding in the core of the k-turn. The A1n nucleotide is highlighted in yellow. This is held by four hydrogen bonds; in addition to the two bonds with G1b that form the trans sugar edge/Hoogsteen edge base pair, there is the critical, conserved A1n:N1–GL1:O2′H interaction, and the A1n:N3–GL1:N2H hydrogen bond. The hydrogen bond between AL3:O2′H and the L1/L2 phosphate proS O is also visible in this image. (B) Hydrogen bonding between the C and NC helices. Two hydrogen bonds are shown. One is from G-1n:O2′H to A2b:N1, and between U3b:O2′ and C-2n:O2′H.