Figure 3.
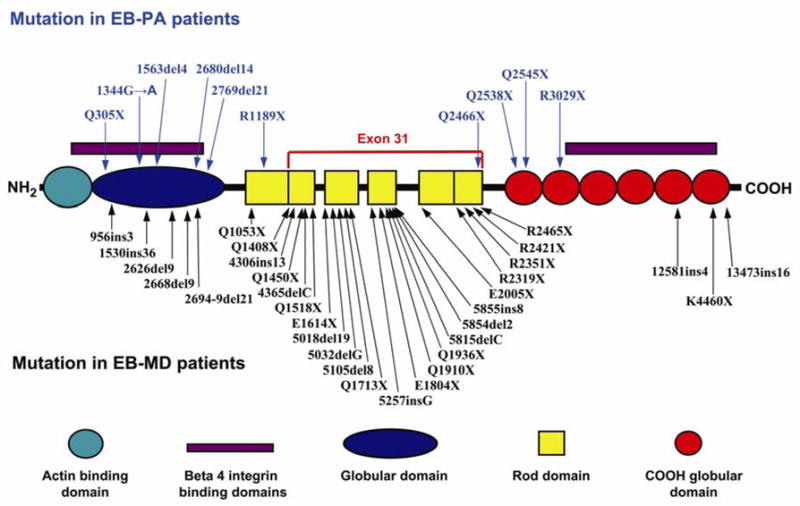
Schematic representation of the domain organization of plectin and mutations in the corresponding gene in patients with EB-PA or with EB-MD. The color code of the domain organization is at the bottom of the figure. The arrows point to the positions of the mutations along the plectin polypeptide. The mutations indicated above the schematic structure are those associated with EB-PA, while those below have been reported to result in EB-MD phenotype. Note the clustering of the mutations causing EB-MD in the rod domain that is encoded by exon 31, while all mutations in EB-PA patients (except one, Q2466X) are outside of exon 31. (Note that the numbering of the mutations may differ from those in original publications due to the fact that the numbering has been adjusted to conform with the plectin sequence in NCBI database entry NM-000445).
