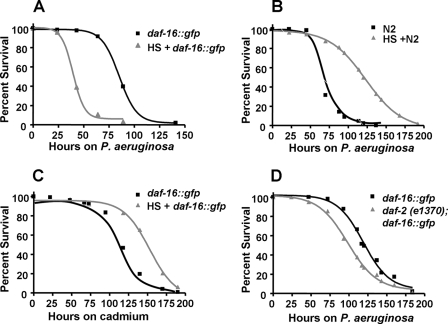
FIGURE 1.
Heat shock treatment of daf-16::gfp animals increases their susceptibility to P. aeruginosa. A, heat-shocked and non-treated daf-16::gfp animals were exposed to P. aeruginosa (p < 0.0001). B, heat-shocked and non-treated wild-type N2 animals were exposed to P. aeruginosa (p < 0.0001). C, heat-shocked and non-treated daf-16::gfp animals were seeded on agar plates containing 100 μm CdCl2 and E. coli (p < 0.0001). D, daf-16::gfp, and daf-2 (e1370);daf-16::gfp animals were exposed to P. aeruginosa (p = 0.0042). Survival assays were performed as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The logrank test, which is equivalent to the Mantel-Heanszel test, was used to compare survival curves. Shown are representative assays of more than six independent experiments (A and B) or two independent experiments (C and D). n = 100 adult nematodes per strain.