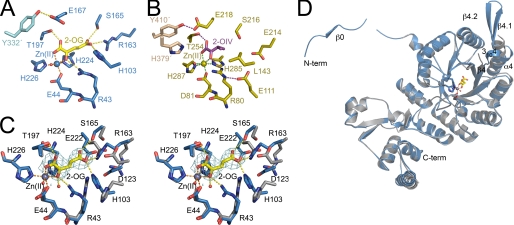
FIGURE 3.
SpHCS active site and 2-OG binding. A, shown is the active site of SpHCS (closed lid conformation; blue carbon atoms) in complex with 2-OG (yellow carbons) and Zn(II) (blue). Orange and yellow dashes represent coordination of the Zn(II) ion and hydrogen bonding to 2-OG, respectively. B, shown is the active site of α-IPMS (gold carbons) in complex with 2-OIV (magenta carbons) and Zn(II) (gold). The coordination of the Zn(II) ion and hydrogen bonds to 2-OIV are colored green and magenta, respectively. C, shown is the stereoview of the active site of the SpHCS 2-OG closed lid complex (rendered as in panel A) overlaid with the SpHCS apoenzyme (gray carbons). The Zn(II) ion and water molecules are represented as gray and red spheres, respectively. Electron density of the Fo − Fc simulated annealing omit map (contoured at 2.5 σ) corresponding to the 2-OG in the closed loop complex is depicted in cyan. D, shown is a ribbon diagram of a monomer of the SpHCS 2-OG closed lid complex (blue) superimposed with the corresponding monomer in the SpHCS apoenzyme (gray). The secondary structural elements that undergo conformational changes between the two structures are denoted.