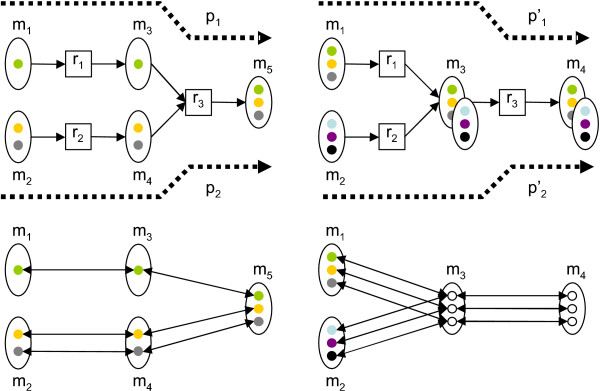
Figure 5.
Reaction and metabolite junctions. Top left: atoms in metabolites m1 and m2 are transferred to atoms in metabolite m5 via two reaction paths p1 = (r1, r3) and p2 = (r2, r3) (indicated by dashed arrows). The paths merge in reaction r3. Pathway P consisting of reactions r1, r2, r3 has ZO (P, S, T) = 1, when atoms of {m1, m2} and {m5} comprise the source and target sets S and T, respectively. Top right: pathway P' = {r1, r2, r3} achieves ZO (P', S, T) = 1 assuming source and target atoms to be all atoms in {m1, m2} and {m4}, respectively. The two reaction paths transferring the atoms,  = (r1, r3) and
= (r1, r3) and  = (r2, r3) merge in metabolite m3. Subsequently, atoms from m1 and m2 are never transferred to the same instance of metabolite m3 via these paths. Bottom left and right: atom graph representations of pathways P (left) and P' (right). Hollow circles denote atoms which can originate from atoms in metabolites m1 or m2.
= (r2, r3) merge in metabolite m3. Subsequently, atoms from m1 and m2 are never transferred to the same instance of metabolite m3 via these paths. Bottom left and right: atom graph representations of pathways P (left) and P' (right). Hollow circles denote atoms which can originate from atoms in metabolites m1 or m2.