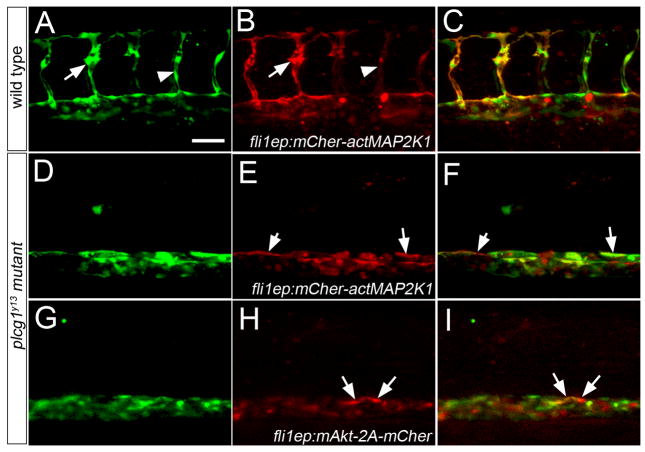
Figure 5.
Activation of Akt or MAPK signaling fails to rescue segmental artery formation in plcg1y13 mutant embryos. A–I. Confocal fluorescent micrographs of trunk blood vessels at 30 hours post fertilization. Anterior is to the left, dorsal is up. Scale bar is 60 μM. A–C. Wild type Tg(fli1a:egfp)y1 embryo co-injected with 25 pg Tol2 transposase mRNA and pTol-fli1ep:mCher-actMAP2K1; arrow denotes excessive filopodial extensions in a sprout expressing high levels of the transgene; arrowhead is a low transgene expressing cell. D–F. Tg(fli1a:egfp)y1;plcg1y13 mutant embryo co-injected with 25 pg Tol2 transposase mRNA and pTol-fli1ep:mCher-actMAP2K1. E, F. Arrows indicate transgene-expressing cells in the dorsal wall of the aorta. G–I. Tg(fli1a:egfp)y1;plcg1y13 mutant embryo co-injected with 25 pg Tol2 transposase mRNA and pTol-fli1ep:mAkt-2A-mCher; H, I. Arrows denote transgene expressing cells in the dorsal aorta.