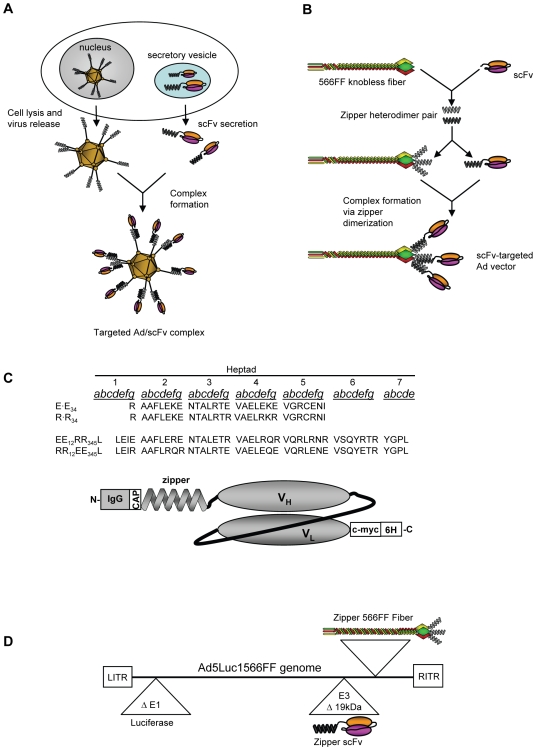
Figure 1. Diagrams depicting our targeting strategy, fiber and scFv configuration, zipper sequences and vector genomes.
(A) Schematic of the proposed Ad vector targeting approach showing Ad-mediated scFv expression and secretion followed by cell lysis and Ad virion release and extracellular formation of a targeted Ad vector/scFv complex. (B) Configuration of heterodimeric zipper domains, wherein one zipper domain is genetically incorporated onto the C-terminus of the knobless 566FF fiber, and its counterpart is fused to the N-terminus of a recombinant scFv molecule. (C) Peptide sequences of the two heterodimeric zipper pairs used. Each of the peptides comprising the pairs E·E34/R·R34, and EE12RR345L/RR12EE345L can associate with its complimentary partner, thereby forming a stable heterodimer. The letters indicate the residue position within each heptad repeat. Also shown is a molecular map of the zipper-scFv fusion proteins showing the N-terminus, IgG-derived secretion signal peptide, a helix cap sequence, zipper sequence, a flexible linker and the scFvG28-5 followed by c-myc and 6His tags at the C-terminus. See main text for additional details. (D) Simplified genomic map of AdLuc1566FF-R/E-G28-5 and AdLuc1566FF-ER/RE-G28-5 vectors showing the CMV/firefly luciferase expression cassette in the deleted E1 region, the zipper-scFv G28-5 open reading frame in place of the 19 kDa protein locus in the E3 region, and zipper-566FF fiber molecule replacing the Ad fiber.