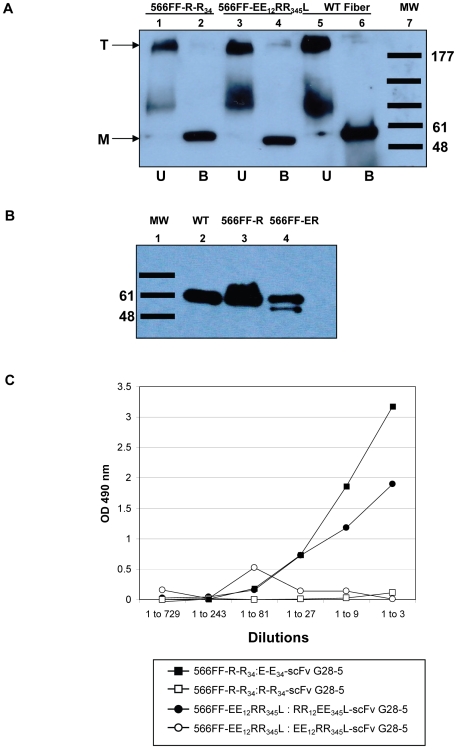
Figure 3. Trimerization profiles of zipper-modified 566FF fiber proteins.
(A) Western blot analysis of lysates of 293T cells transfected with expression vectors expressing zipper-modified 566FF fiber proteins. Protein samples in Laemmli buffer were separated by SDS-PAGE with prior heat denaturation by boiling (B, boiled) or without boiling (U, unboiled). Following transfer of proteins to PVDF membrane, proteins were then probed with an anti-fiber monoclonal antibody that recognizes the fiber tail. Lanes 1 and 2 contains 566FF-R-R12 fibers, lanes 3 and 4 the 566FF-EE12RR345L fibers and lanes 5 and 6 wild type Ad5 fiber. Fiber monomers (M) and trimers (T) are indicated. Molecular mass markers indicate kilodaltons. (B) Western blot analysis of fibers from virions purified on 293 cells and containing a single genetically encoded fiber. Lane 2 contains WT Ad5 fiber, Lane 3 is 566FF-R and lane 4 is 566FF-ER. Each lane contained 5×109 viral particles. (C) ELISA-based binding assay of zipper-tagged 566FF fibers with zipper-scFv G28-5. Zipper-scFv proteins expressed by Ad vectors cells were purified by immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography and adsorbed into wells of a 96-well ELISA plate. Dilutions of equal amounts of cell lysate from 293T cells transfected with plasmids encoding the 566FF-zipper proteins were added to the wells. The formation of stable complexes was demonstrated by detection of the scFv-bound 566FF fiber proteins with an anti-fiber 4D2 monoclonal antibody.