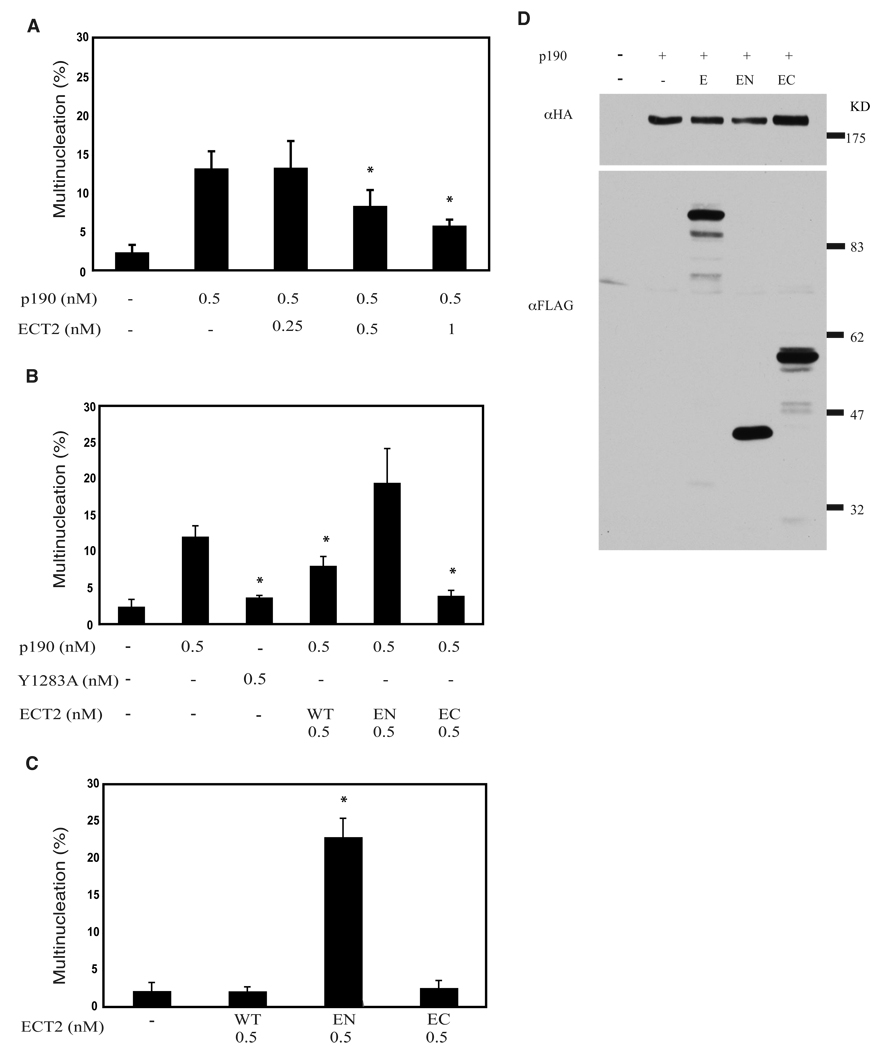
Fig. 1. Coexpression of ECT2 RhoGEF reduces p190-induced multinucleation.
(A) Coexpression of ECT2 reduces p190-induced multinucleation in a dose-dependent manner. Varied amounts of wild type, FLAG-tagged ECT2 plasmid (as indicated) were co-transfected with a constant amount of HA-tagged p190 plasmid into Hela cells as described in Methods. Forty-eight hrs later, cells were analyzed by immunofluorescence for the presence of HA-p190- and Flag-ECT2- expressing cells that displayed a multinucleated phenotype. Data are presented as the Mean ± SEM for n≥3. * represents p<0.05.
(B) Full length and constitutively active FLAG-ECT2 reduce multinucleation in HA-p190-overexpressing cells. Equal moles of plasmids encoding wild type or mutant FLAG-ECT2 were co-expressed with HA-p190 in HeLa cells, and transfected cells were analyzed as in Panel A. Data are presented as Mean ± SEM for n≥3. * represents p<0.05.
(C) Dominant negative ECT2 induces multinucleation. Equal moles of plasmids encoding wild type or mutant Flag ECT2 were transfected into Hela cells, and transfected cells were analyzed as in Panel A. Data are presented as the Mean ± SEM for n≥3. * represents p<0.05.
(D) Western blotting of whole cell lysates from HA-p190 and FLAG-ECT2 co-expressing cells analyzed in Panel B. Thirty µg whole cell lysates were immunoblotted with anti-FLAG antibody to detect levels of E (ECT2), EN (ECT2N), and EC (ECT2C), and with anti-HA antibody to detect p190.