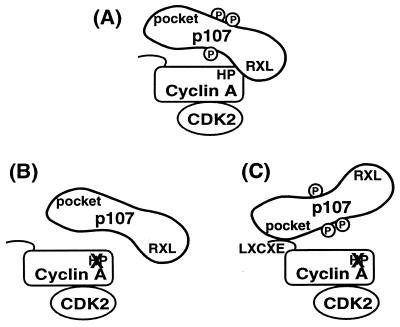
Figure 5.
A model for cyclin A-cdk2 recognition of a substrate, p107. (A) The RXL motif in p107 normally contacts the hydrophobic patch in cyclin A. (B) Mutation of the hydrophobic patch on cyclin A dramatically reduces binding to and phosphorylation of p107. (C) Binding between p107 and a hydrophobic patch mutant of cyclin A can be restored by addition of the p107 pocket-binding sequence, LXCXE, to cyclin A. Restoration of binding is sufficient to rescue phosphorylation. Thus, a specific trajectory between substrate binding and the kinase active site is not necessary for phosphorylation, and the purpose of substrate binding is to increase the local concentration available to the kinase.