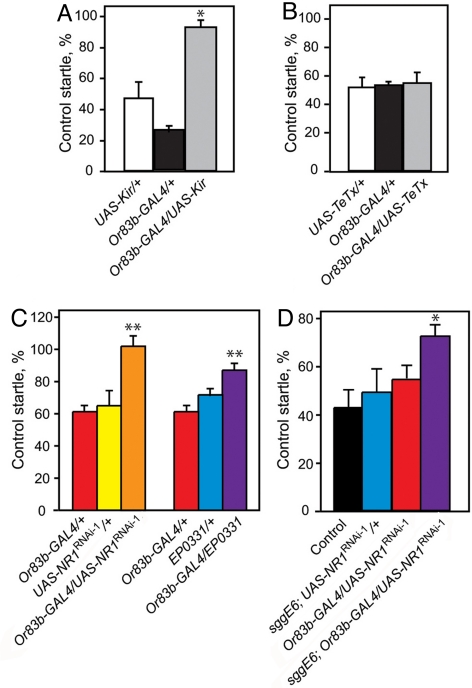
Fig. 6.
Electrical silencing protects ORNs from ethanol-induced damage. (A) Expression of Kir2.1 (UAS-Kir) in ORNs using the Or83b-GAL4 driver protects flies from ethanol-induced loss of olfactory startle (n = 6, *, P < 0.01). Data are presented as % startle retained by preexposed flies compared to unexposed flies of the same genotype. (B) Synaptic silencing by expression of tetanus-toxin light chain (TeTx) had no protective effect (n = 4). (C) Double-stranded RNA interference (UAS-NR1RNAi) and antisense dNR1 (EP0331) expression protects flies against ethanol-induced startle loss (n = 5, **, P < 0.01, *, P < 0.05). (D) Combining mutation of sgg with UAS-NR1RNAi driven by Or83b-GAL4 results in a supra-additive protective effect. While sggE6 and Or83b-GAL4/UAS-NR1RNAi flies both demonstrate weak resistance, the combination results in a synergistic effect (n = 3, *, P < 0.05).