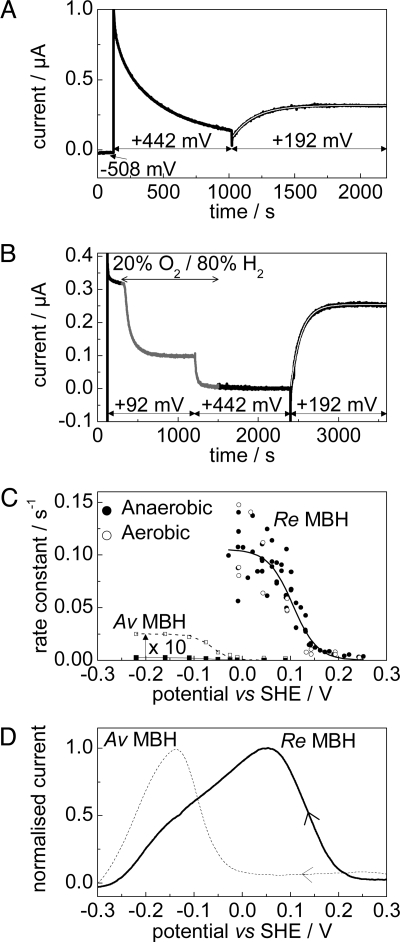
Fig. 3.
Reactivation of aerobically and anaerobically inactivated states of Re MBH. (A and B) Typical experiments to measure the rate of reactivation of Re MBH under 100% H2 following anaerobic (A) and aerobic (B) inactivation. In these examples, reactivation was measured at +0.192 V. (C) Rates of reactivation as a function of potential with a fit to the data overlaid. Data for the reactivation of Av MBH from the Unready state (filled squares, taken from reference 16, pH 6, 45° C) are also shown, and have been multiplied by 10 for clarity (unfilled squares). Sigmoidal fits are also shown. (D) Voltammograms (100% H2, 0.1 mV s−1) of Re MBH (bold) and Av MBH (dashed), showing recovery after aerobic inactivation at 392 mV under N2. All at pH 5.5, 10° C, electrode rotation rate = 2,500 rpm.