Figure 18.1.
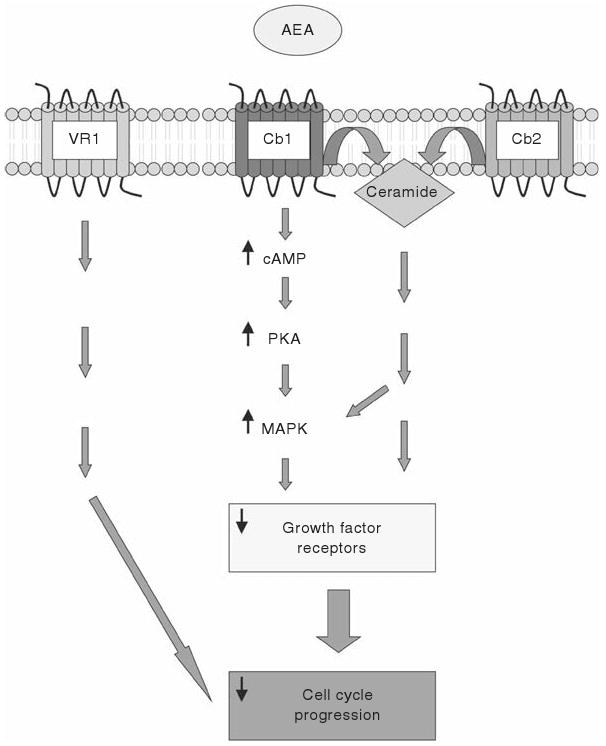
Schematic diagram of the cannabinoid receptor-dependent mechanisms whereby AEA leads to tumor growth suppression and/or cell death. AEA may act via the Cb1 receptor to activate the cAMP/PKA/MAPK pathway or to increase the production of ceramide. These effects ultimately result in a decrease in the expression of various growth factor receptors and decrease cell cycle progression. Alternatively, AEA may activate either Cb2 or VR1 to elicit a similar response, although the mechanism by which this occurs is not clear.
